この記事では、二分探索アルゴリズムについて説明します。検索は、リスト内の特定の要素を見つけるプロセスです。要素がリストに存在する場合、プロセスは成功と呼ばれ、プロセスはその要素の場所を返します。それ以外の場合、検索は失敗したと呼ばれます。
線形検索と二分検索は、2 つの一般的な検索手法です。ここでは二分探索アルゴリズムについて説明します。
二分探索は、ソートされたリストに対して効率的に機能する検索手法です。したがって、二分探索手法を使用してリスト内の要素を検索するには、リストがソートされていることを確認する必要があります。
二分探索は、リストを 2 つの半分に分割し、項目をリストの中央の要素と比較する分割統治アプローチに従います。一致が見つかった場合は、中央の要素の位置が返されます。それ以外の場合は、試合を通じて生成された結果に応じて、どちらかの半分を検索します。
注: 二分検索は、ソートされた配列要素に対して実装できます。リスト要素がソートされた方法で配置されていない場合は、まずそれらをソートする必要があります。
次に、二分探索のアルゴリズムを見てみましょう。
アルゴリズム
Binary_Search(a, lower_bound, upper_bound, val) // 'a' is the given array, 'lower_bound' is the index of the first array element, 'upper_bound' is the index of the last array element, 'val' is the value to search Step 1: set beg = lower_bound, end = upper_bound, pos = - 1 Step 2: repeat steps 3 and 4 while beg val set end = mid - 1 else set beg = mid + 1 [end of if] [end of loop] Step 5: if pos = -1 print 'value is not present in the array' [end of if] Step 6: exit
二分探索の仕組み
ここで、二分探索アルゴリズムの仕組みを見てみましょう。
二分探索アルゴリズムの動作を理解するために、ソートされた配列を見てみましょう。例を挙げて二分探索の仕組みを理解しやすくします。
二分探索アルゴリズムを実装するには 2 つの方法があります。
- 反復法
- 再帰的メソッド
二分探索の再帰的方法は、分割統治アプローチに従います。
配列の要素を次のようにします -
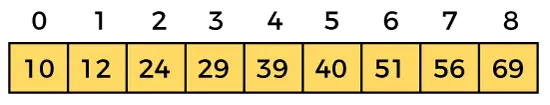
検索する要素を次のようにします。 K = 56
レジスタ転送ロジック
を計算するには、以下の式を使用する必要があります。 半ば 配列の -
Javaがmysqlに接続する
mid = (beg + end)/2
したがって、指定された配列では -
懇願する = 0
終わり = 8
半ば = (0 + 8)/2 = 4。つまり、4 は配列の中央です。



これで、検索する要素が見つかりました。したがって、アルゴリズムは一致した要素のインデックスを返します。
二分探索の複雑さ
ここで、最良の場合、平均的な場合、および最悪の場合における二分探索の時間計算量を見てみましょう。また、二分探索の空間の複雑さも見ていきます。
1. 時間計算量
| 場合 | 時間計算量 |
|---|---|
| 最良の場合 | ○(1) |
| 平均的なケース | O(ログン) |
| 最悪の場合 | O(ログン) |
2. 空間の複雑さ
| 空間の複雑さ | ○(1) |
- 二分探索の空間計算量は O(1) です。
二分探索の実装
ここで、さまざまなプログラミング言語での二分探索のプログラムを見てみましょう。
プログラム: C言語で二分探索を実装するプログラムを書きます。
#include int binarySearch(int a[], int beg, int end, int val) { int mid; if(end >= beg) { mid = (beg + end)/2; /* if the item to be searched is present at middle */ if(a[mid] == val) { return mid+1; } /* if the item to be searched is smaller than middle, then it can only be in left subarray */ else if(a[mid] <val) { return binarysearch(a, mid+1, end, val); } * if the item to be searched is greater than middle, then it can only in right subarray else beg, mid-1, -1; int main() a[]="{11," 14, 25, 30, 40, 41, 52, 57, 70}; given array val="40;" value n="sizeof(a)" sizeof(a[0]); size of res="binarySearch(a," 0, n-1, store result printf('the elements are - '); for (int i="0;" < n; i++) printf('%d ', a[i]); printf('
element %d', (res="=" -1) not present array'); at %d position array', res); 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/10/binary-search-algorithm-5.webp" alt="Binary Search Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement Binary search in C++.</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; int binarySearch(int a[], int beg, int end, int val) { int mid; if(end >= beg) { mid = (beg + end)/2; /* if the item to be searched is present at middle */ if(a[mid] == val) { return mid+1; } /* if the item to be searched is smaller than middle, then it can only be in left subarray */ else if(a[mid] <val) { return binarysearch(a, mid+1, end, val); } * if the item to be searched is greater than middle, then it can only in right subarray else beg, mid-1, -1; int main() a[]="{10," 12, 24, 29, 39, 40, 51, 56, 70}; given array val="51;" value n="sizeof(a)" sizeof(a[0]); size of res="binarySearch(a," 0, n-1, store result cout<<'the elements are - '; for (int i="0;" < n; i++) cout< <a[i]<<' cout<<'
element '<<val; (res="=" -1) not present array'; at '<<res<<' position 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/10/binary-search-algorithm-6.webp" alt="Binary Search Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement Binary search in C#.</p> <pre> using System; class BinarySearch { static int binarySearch(int[] a, int beg, int end, int val) { int mid; if(end >= beg) { mid = (beg + end)/2; if(a[mid] == val) { return mid+1; /* if the item to be searched is present at middle */ } /* if the item to be searched is smaller than middle, then it can only be in left subarray */ else if(a[mid] <val) { return binarysearch(a, mid+1, end, val); } * if the item to be searched is greater than middle, then it can only in right subarray else beg, mid-1, -1; static void main() int[] a="{9," 11, 23, 28, 38, 45, 50, 56, 70}; given array int val="70;" value n="a.Length;" size of res="binarySearch(a," 0, n-1, store result console.write('the elements are - '); for (int i="0;" < n; i++) console.write(a[i] + ' console.writeline(); console.writeline('element (res="=" -1) not present array'); at position pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/10/binary-search-algorithm-7.webp" alt="Binary Search Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement Binary search in Java.</p> <pre> class BinarySearch { static int binarySearch(int a[], int beg, int end, int val) { int mid; if(end >= beg) { mid = (beg + end)/2; if(a[mid] == val) { return mid+1; /* if the item to be searched is present at middle */ } /* if the item to be searched is smaller than middle, then it can only be in left subarray */ else if(a[mid] <val) { return binarysearch(a, mid+1, end, val); } * if the item to be searched is greater than middle, then it can only in right subarray else beg, mid-1, -1; public static void main(string args[]) int a[]="{8," 10, 22, 27, 37, 44, 49, 55, 69}; given array val="37;" value n="a.length;" size of res="binarySearch(a," 0, n-1, store result system.out.print('the elements are: '); for (int i="0;" < n; i++) system.out.print(a[i] + ' system.out.println(); system.out.println('element is: (res="=" -1) not present array'); at position pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/10/binary-search-algorithm-8.webp" alt="Binary Search Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement Binary search in PHP.</p> <pre> = $beg) { $mid = floor(($beg + $end)/2); if($a[$mid] == $val) { return $mid+1; /* if the item to be searched is present at middle */ } /* if the item to be searched is smaller than middle, then it can only be in left subarray */ else if($a[$mid] <$val) { return binarysearch($a, $mid+1, $end, $val); } * if the item to be searched is greater than middle, then it can only in right subarray else $beg, $mid-1, -1; $a="array(7," 9, 21, 26, 36, 43, 48, 54, 68); given array $val="68;" value $n="sizeof($a);" size of $res="binarySearch($a," 0, $n-1, store result echo 'the elements are: '; for ($i="0;" $i < $n; $i++) ' , $a[$i]; <br>' , 'Element to be searched is: ' , $val; if ($res == -1) echo ' <br>' , 'Element is not present in the array'; else echo ' <br>' , 'Element is present at ' , $res , ' position of array'; ?> </$val)></pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/10/binary-search-algorithm-9.webp" alt="Binary Search Algorithm"> <p>So, that's all about the article. Hope the article will be helpful and informative to you.</p> <hr></val)></pre></val)></pre></val)></pre></val)> 出力

それでは、この記事については以上です。この記事があなたにとって有益で有益であることを願っています。
