この記事では、クイックソート アルゴリズムについて説明します。クイックソートの作業手順も簡単です。この記事は、試験問題としてクイックソートが出題される可能性がある学生にとって、非常に役立ち、興味深いものとなるでしょう。したがって、そのテーマについて話し合うことが重要です。
並べ替えは、アイテムを体系的に配置する方法です。クイックソートは、広く使用されている並べ替えアルゴリズムです。 nログn n 要素の配列をソートする場合の平均的な比較。これは、より高速で効率の高い並べ替えアルゴリズムです。このアルゴリズムは分割統治アプローチに従っています。分割統治は、アルゴリズムを部分問題に分割し、その部分問題を解決し、その結果を結合して元の問題を解決する手法です。
JavaでCSVを読み取る
分ける: Divide では、まずピボット要素を選択します。その後、左側のサブ配列の各要素がピボット要素以下となり、右側のサブ配列の各要素がピボット要素より大きくなるように、配列を 2 つのサブ配列に分割または再配置します。
征服する: クイックソートを使用して 2 つの部分配列を再帰的にソートします。
組み合わせる: すでにソート済みの配列を結合します。
クイックソートは要素をピボットとして選択し、選択したピボット要素を中心に指定された配列を分割します。クイック ソートでは、大きな配列が 2 つの配列に分割され、1 つは指定された値 (ピボット) より小さい値を保持し、もう 1 つの配列はピボットより大きい値を保持します。
その後、左右のサブ配列も同じアプローチを使用して分割されます。これは、単一の要素がサブ配列に残るまで継続されます。
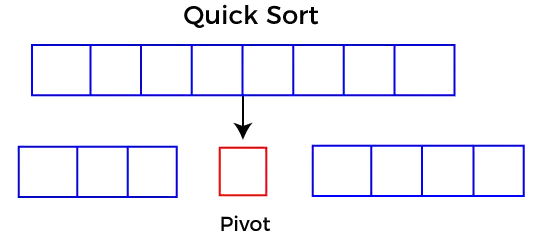
ピボットの選択
クイックソートを迅速に実装するには、適切なピボットを選択することが必要です。ただし、適切なピボットを決定するのが一般的です。ピボットを選択する方法のいくつかは次のとおりです。
- ピボットはランダムにすることができます。つまり、指定された配列からランダムなピボットを選択します。
- ピボットは、指定された配列の右端の要素または左端の要素のいずれかになります。
- ピボット要素として中央値を選択します。
アルゴリズム
アルゴリズム:
QUICKSORT (array A, start, end) { 1 if (start <end) 2 3 4 5 6 { p="partition(A," start, end) quicksort (a, - 1) + 1, } < pre> <p> <strong>Partition Algorithm:</strong> </p> <p>The partition algorithm rearranges the sub-arrays in a place.</p> <pre> PARTITION (array A, start, end) { 1 pivot ? A[end] 2 i ? start-1 3 for j ? start to end -1 { 4 do if (A[j] <pivot) 1 5 6 7 8 9 { then i ? + swap a[i] with a[j] }} a[i+1] a[end] return i+1 } < pre> <h2>Working of Quick Sort Algorithm</h2> <p>Now, let's see the working of the Quicksort Algorithm.</p> <p>To understand the working of quick sort, let's take an unsorted array. It will make the concept more clear and understandable.</p> <p>Let the elements of array are -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-2.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>In the given array, we consider the leftmost element as pivot. So, in this case, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 27 and a[pivot] = 24.</p> <p>Since, pivot is at left, so algorithm starts from right and move towards left.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-3.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] <a[right], so algorithm moves forward one position towards left, i.e. -< p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-4.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 19, and a[pivot] = 24.</p> <p>Because, a[pivot] > a[right], so, algorithm will swap a[pivot] with a[right], and pivot moves to right, as -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-5.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 19, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. Since, pivot is at right, so algorithm starts from left and moves to right.</p> <p>As a[pivot] > a[left], so algorithm moves one position to right as -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-6.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 9, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] > a[left], so algorithm moves one position to right as -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-7.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[left] = 29, a[right] = 24, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] <a[left], so, swap a[pivot] and a[left], now pivot is at left, i.e. -< p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-8.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Since, pivot is at left, so algorithm starts from right, and move to left. Now, a[left] = 24, a[right] = 29, and a[pivot] = 24. As a[pivot] <a[right], so algorithm moves one position to left, as -< p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-9.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 24, and a[right] = 14. As a[pivot] > a[right], so, swap a[pivot] and a[right], now pivot is at right, i.e. -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-10.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 14, and a[right] = 24. Pivot is at right, so the algorithm starts from left and move to right.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-11.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, a[pivot] = 24, a[left] = 24, and a[right] = 24. So, pivot, left and right are pointing the same element. It represents the termination of procedure.</p> <p>Element 24, which is the pivot element is placed at its exact position.</p> <p>Elements that are right side of element 24 are greater than it, and the elements that are left side of element 24 are smaller than it.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-12.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>Now, in a similar manner, quick sort algorithm is separately applied to the left and right sub-arrays. After sorting gets done, the array will be -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-13.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <h2>Quicksort complexity</h2> <p>Now, let's see the time complexity of quicksort in best case, average case, and in worst case. We will also see the space complexity of quicksort.</p> <h3>1. Time Complexity</h3> <table class="table"> <tr> <th>Case</th> <th>Time Complexity</th> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Best Case</strong> </td> <td>O(n*logn)</td> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Average Case</strong> </td> <td>O(n*logn)</td> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Worst Case</strong> </td> <td>O(n<sup>2</sup>)</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <tr><td>Best Case Complexity -</td> In Quicksort, the best-case occurs when the pivot element is the middle element or near to the middle element. The best-case time complexity of quicksort is <strong>O(n*logn)</strong> . </tr><tr><td>Average Case Complexity -</td> It occurs when the array elements are in jumbled order that is not properly ascending and not properly descending. The average case time complexity of quicksort is <strong>O(n*logn)</strong> . </tr><tr><td>Worst Case Complexity -</td> In quick sort, worst case occurs when the pivot element is either greatest or smallest element. Suppose, if the pivot element is always the last element of the array, the worst case would occur when the given array is sorted already in ascending or descending order. The worst-case time complexity of quicksort is <strong>O(n<sup>2</sup>)</strong> . </tr></ul> <p>Though the worst-case complexity of quicksort is more than other sorting algorithms such as <strong>Merge sort</strong> and <strong>Heap sort</strong> , still it is faster in practice. Worst case in quick sort rarely occurs because by changing the choice of pivot, it can be implemented in different ways. Worst case in quicksort can be avoided by choosing the right pivot element.</p> <h3>2. Space Complexity</h3> <table class="table"> <tr> <td> <strong>Space Complexity</strong> </td> <td>O(n*logn)</td> </tr> <tr> <td> <strong>Stable</strong> </td> <td>NO</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <li>The space complexity of quicksort is O(n*logn).</li> </ul> <h2>Implementation of quicksort</h2> <p>Now, let's see the programs of quicksort in different programming languages.</p> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quicksort in C language.</p> <pre> #include /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ int partition (int a[], int start, int end) { int pivot = a[end]; // pivot element int i = (start - 1); for (int j = start; j <= 27 end - 1; j++) { if current element is smaller than the pivot (a[j] < pivot) i++; increment index of int t="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="t;" } a[i+1]="a[end];" a[end]="t;" return (i + 1); * function to implement quick sort void quick(int a[], start, end) a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, (start p="partition(a," end); partitioning quick(a, 1, print an array printarr(int n) i; for i n; i++) printf('%d ', a[i]); main() 24, 9, 29, 14, 19, }; n="sizeof(a)" sizeof(a[0]); printf('before sorting elements are
'); printarr(a, n); 0, printf('
after 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-14.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quick sort in C++ language.</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ int partition (int a[], int start, int end) { int pivot = a[end]; // pivot element int i = (start - 1); for (int j = start; j <= 26 end - 1; j++) { if current element is smaller than the pivot (a[j] < pivot) i++; increment index of int t="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="t;" } a[i+1]="a[end];" a[end]="t;" return (i + 1); * function to implement quick sort void quick(int a[], start, end) a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, (start p="partition(a," end); partitioning quick(a, 1, print an array printarr(int n) i; for i n; i++) cout< <a[i]<< ' '; main() 23, 8, 28, 13, 18, }; n="sizeof(a)" sizeof(a[0]); cout<<'before sorting elements are
'; printarr(a, n); 0, cout<<'
after 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-15.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quicksort in python.</p> <pre> #function that consider last element as pivot, #place the pivot at its exact position, and place #smaller elements to left of pivot and greater #elements to right of pivot. def partition (a, start, end): i = (start - 1) pivot = a[end] # pivot element for j in range(start, end): # If current element is smaller than or equal to the pivot if (a[j] <= 1 pivot): i="i" + a[i], a[j]="a[j]," a[i] a[i+1], a[end]="a[end]," a[i+1] return (i 1) # function to implement quick sort def quick(a, start, end): a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, end="Ending" index if (start < p="partition(a," end) is partitioning - 1, printarr(a): print the array for in range(len(a)): (a[i], ) a="[68," 13, 49, 58] print('before sorting elements are ') printarr(a) 0, len(a)-1) print('
after pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-16.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quicksort in Java.</p> <pre> public class Quick { /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ int partition (int a[], int start, int end) { int pivot = a[end]; // pivot element int i = (start - 1); for (int j = start; j <= 25 end - 1; j++) { if current element is smaller than the pivot (a[j] < pivot) i++; increment index of int t="a[i];" a[i]="a[j];" a[j]="t;" } a[i+1]="a[end];" a[end]="t;" return (i + 1); * function to implement quick sort void quick(int a[], start, end) a[]="array" be sorted, start="Starting" index, (start p="partition(a," end); partitioning quick(a, 1, print an array printarr(int n) i; for i n; i++) system.out.print(a[i] ' '); public static main(string[] args) 13, 18, 27, 2, 19, }; n="a.length;" system.out.println('
before sorting elements are q1="new" quick(); q1.printarr(a, n); q1.quick(a, 0, system.out.println('
after system.out.println(); pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <p>After the execution of above code, the output will be -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-17.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p> <strong>Program:</strong> Write a program to implement quick sort in php.</p> <pre> <?php /* function that consider last element as pivot, place the pivot at its exact position, and place smaller elements to left of pivot and greater elements to right of pivot. */ function partition (&$a, $start, $end) { $pivot = $a[$end]; // pivot element $i = ($start - 1); for ($j = $start; $j <= $end - 1; $j++) { // If current element is smaller than the pivot if ($a[$j] < $pivot) { $i++; // increment index of smaller element $t = $a[$i]; $a[$i] = $a[$j]; $a[$j] = $t; } } $t = $a[$i+1]; $a[$i+1] = $a[$end]; $a[$end] = $t; return ($i + 1); } /* function to implement quick sort */ function quick(&$a, $start, $end) /* a[] = array to be sorted, start = Starting index, end = Ending index */ { if ($start < $end) { $p = partition($a, $start, $end); //p is partitioning index quick($a, $start, $p - 1); quick($a, $p + 1, $end); } } function printArray($a, $n) { for($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) { print_r($a[$i]); echo ' '; } } $a = array( 89, 47, 2, 17, 8, 19 ); $n = count($a); echo 'Before sorting array elements are - <br>'; printArray($a, $n); quick($a, 0, $n - 1); echo ' <br> After sorting array elements are - <br>'; printArray($a, $n); ?> </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <p>After the execution of above code, the output will be -</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/ds-tutorial/75/quick-sort-algorithm-18.webp" alt="Quick Sort Algorithm"> <p>So, that's all about the article. Hope the article will be helpful and informative to you.</p> <p>This article was not only limited to the algorithm. Along with the algorithm, we have also discussed the quick sort complexity, working, and implementation in different programming languages.</p> <hr></=></pre></=></pre></=></pre></=></pre></a[right],></p></a[left],></p></a[right],></p></pivot)></pre></end)> 出力
上記のコードを実行すると、出力は次のようになります -

それでは、この記事については以上です。この記事があなたにとって有益で有益であることを願っています。
この記事はアルゴリズムだけに限定されたものではありません。アルゴリズムに加えて、クイック ソートの複雑さ、動作、さまざまなプログラミング言語での実装についても説明しました。
.tostring java
