多次元配列。最も一般的に使用される多次元配列は、2 次元配列と 3 次元配列です。高次元の配列は基本的に配列の配列であると言えます。 2D 配列の非常に一般的な例はチェス盤です。チェス盤は、64 個の 1×1 の正方形のボックスを含むグリッドです。 2D 配列も同様に視覚化できます。 2D 配列では、すべての要素が行番号と列番号に関連付けられます。 2D 配列の要素にアクセスすることは、行番号と列番号の両方を使用して Excel ファイルのレコードにアクセスすることと似ています。 2D 配列は、三目並べゲームやチェスの実装時、さらには画像ピクセルの保存時にも役立ちます。
Java での 2 次元配列の宣言:
任意の 2 次元配列は次のように宣言できます。
構文:
データ型 配列名[][]; (または) data_type[][] array_name;
- data_type: Java は静的に型付けされた言語であるため (つまり、値を割り当てる前に変数が宣言されることが期待されます)。したがって、データ型を指定すると、受け入れる要素の型が決まります。例えば整数値のみを格納する場合、データ型は int として宣言されます。 array_name: 2 次元配列に与えられる名前です。例えば科目、学生、果物、学科など
注記: 2D 配列を宣言するときに、data_type の後に [ ][ ] を書くことも、array_name の後に [ ][ ] を書くこともできます。
ジャワ
// java program showing declaration of arrays> import> java.io.*;> > class> GFG {> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> > >int>[][] integer2DArray;>// 2D integer array> >String[][] string2DArray;>// 2D String array> >double>[][] double2DArray;>// 2D double array> >boolean>[][] boolean2DArray;>// 2D boolean array> >float>[][] float2DArray;>// 2D float array> >double>[][] double2DArray;>// 2D double array> >}> }> |
>
>
Java での 2 次元配列の初期化のさまざまなアプローチ:
データ型[][] 配列名 = 新しい データタイプ[行数][列数];
2D 配列内の要素の合計は、(no_of_rows) * (no_of_columns) に等しくなります。
- no_of_rows: 配列内の行数。例えばno_of_rows = 3 の場合、配列には 3 つの行が含まれます。 no_of_columns: 配列内の列の数。例えばno_of_columns = 4 の場合、配列には 4 つの列が含まれます。
配列初期化の上記の構文は、指定されたデータ型に従って、すべての配列要素にデフォルト値を割り当てます。
以下は、2D 配列を初期化するためのさまざまなアプローチの実装です。
リスト文字列Java
アプローチ 1:
ジャワ
// java program to initialize a 2D array> import> java.io.*;> > class> GFG {> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Declaration along with initialization> >// 2D integer array with 5 rows and 3 columns> >// integer array elements are initialized with 0> >int>[][] integer2DArray =>new> int>[>5>][>3>];> >System.out.println(> >'Default value of int array element: '> >+ integer2DArray[>0>][>0>]);> > >// 2D String array with 4 rows and 4 columns> >// String array elements are initialized with null> >String[][] string2DArray =>new> String[>4>][>4>];> >System.out.println(> >'Default value of String array element: '> >+ string2DArray[>0>][>0>]);> > >// 2D boolean array with 3 rows and 5 columns> >// boolean array elements are initialized with false> >boolean>[][] boolean2DArray =>new> boolean>[>4>][>4>];> >System.out.println(> >'Default value of boolean array element: '> >+ boolean2DArray[>0>][>0>]);> > >// 2D char array with 10 rows and 10 columns> >// char array elements are initialized with> >// 'u0000'(null character)> >char>[][] char2DArray =>new> char>[>10>][>10>];> >System.out.println(> >'Default value of char array element: '> >+ char2DArray[>0>][>0>]);> > >// First declaration and then initialization> >int>[][] arr;>// declaration> > >// System.out.println('arr[0][0]: '+ arr[0][0]);> >// The above line will throw an error, as we have> >// only declared the 2D array, but not initialized> >// it.> >arr =>new> int>[>5>][>3>];>// initialization> >System.out.println(>'arr[0][0]: '> + arr[>0>][>0>]);> >}> }> |
>
>
注記: 2D 配列を初期化するときは、常に最初の次元 (行数) を指定する必要がありますが、2 番目の次元 (列数) は省略できます。
以下のコード スニペットでは、列数を指定していません。ただし、Java コンパイラは、列内の要素の数をチェックすることでサイズを操作できるほど賢いです。
ジャワ
import> java.io.*;> > class> GFG {> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// The line below will throw an error, as the first> >// dimension(no. of rows) is not specified> >int>[][] arr =>new> int>[][>3>];> > >// The line below will execute without any error, as> >// the first dimension(no. of rows) is specified> >int>[][] arr =>new> int>[>2>][];> >}> }> |
>
>
行番号と列番号を使用して、2D 配列の任意の要素にアクセスできます。
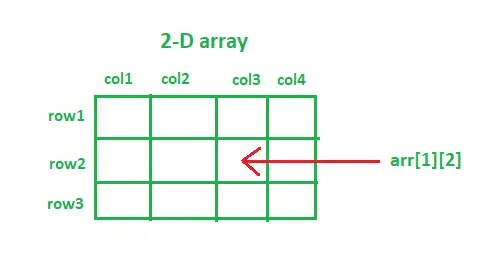
アプローチ 2:
以下のコード スニペットでは、行数と列数を指定していません。ただし、Java コンパイラは、行と列内の要素の数をチェックすることでサイズを操作できるほど賢いです。
ジャワ
import> java.io.*;> > class> GFG {> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >String[][] subjects = {> >{>'Data Structures & Algorithms'>,> >'Programming & Logic'>,>'Software Engineering'>,> >'Theory of Computation'> },>// row 1> > >{>'Thermodynamics'>,>'Metallurgy'>,> >'Machine Drawing'>,> >'Fluid Mechanics'> },>// row2> > >{>'Signals and Systems'>,>'Digital Electronics'>,> >'Power Electronics'> }>// row3> >};> > >System.out.println(> >'Fundamental Subject in Computer Engineering: '> >+ subjects[>0>][>0>]);> >System.out.println(> >'Fundamental Subject in Mechanical Engineering: '> >+ subjects[>1>][>3>]);> >System.out.println(> >'Fundamental Subject in Electronics Engineering: '> >+ subjects[>2>][>1>]);> >}> }> |
ポリモーフィズムJava
>
Cプログラミングを含む
>出力
Fundamental Subject in Computer Engineering: Data Structures & Algorithms Fundamental Subject in Mechanical Engineering: Fluid Mechanics Fundamental Subject in Electronics Engineering: Digital Electronics>
アプローチ 3:
さらに、配列の各要素を個別に初期化できます。以下のコード スニペットを見てください。
ジャワ
import> java.io.*;> import> java.util.*;> > class> GFG {> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >int>[][] scores =>new> int>[>2>][>2>];> >// Initializing array element at position[0][0],> >// i.e. 0th row and 0th column> >scores[>0>][>0>] =>15>;> >// Initializing array element at position[0][1],> >// i.e. 0th row and 1st column> >scores[>0>][>1>] =>23>;> >// Initializing array element at position[1][0],> >// i.e. 1st row and 0th column> >scores[>1>][>0>] =>30>;> >// Initializing array element at position[1][1],> >// i.e. 1st row and 1st column> >scores[>1>][>1>] =>21>;> > >// printing the array elements individually> >System.out.println(>'scores[0][0] = '> >+ scores[>0>][>0>]);> >System.out.println(>'scores[0][1] = '> >+ scores[>0>][>1>]);> >System.out.println(>'scores[1][0] = '> >+ scores[>1>][>0>]);> >System.out.println(>'scores[1][1] = '> >+ scores[>1>][>1>]);> >// printing 2D array using Arrays.deepToString() method> >System.out.println(> >'Printing 2D array using Arrays.deepToString() method: '>);> >System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(scores));> >}> }> |
>
>出力
scores[0][0] = 15 scores[0][1] = 23 scores[1][0] = 30 scores[1][1] = 21 Printing 2D array using Arrays.deepToString() method: [[15, 23], [30, 21]]>
アプローチ 4
2D 配列のサイズが大きすぎる場合、配列の初期化に上記のアプローチを使用するのは面倒な作業になります。効率的な方法は、大きな 2D 配列の場合、for ループを使用して配列要素を初期化することです。
ジャワ
import> java.io.*;> > class> GFG {> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >int> rows =>80>, columns =>5>;> >int>[][] marks =>new> int>[rows][columns];> > >// initializing the array elements using for loop> >for> (>int> i =>0>; i for (int j = 0; j marks[i][j] = i + j; } } // printing the first three rows of marks array System.out.println('First three rows are: '); for (int i = 0; i <3; i++) { for (int j = 0; j System.out.printf(marks[i][j] + ' '); } System.out.println(); } } }> |
>
>出力
First three rows are: 0 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 6>
注記: arr を使用できます。 length 関数を使用して行 (1 次元) のサイズを確認し、arr[0].length 関数を使用して列のサイズ (2 次元) を確認します。
アプローチ 5: (ギザギザ配列)
特定のシナリオでは、すべての行に異なる数の列を含める必要がある場合があります。このタイプの配列は、 Jagged Array と呼ばれます。
ジャワ
import> java.io.*;> > class> GFG {> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// declaring a 2D array with 2 rows> >int> jagged[][] =>new> int>[>2>][];> > >// not specifying the 2nd dimension,> >// and making it as jagged array> >// first row has 2 columns> >jagged[>0>] =>new> int>[>2>];> >// second row has 4 columns> >jagged[>1>] =>new> int>[>4>];> >// Initializing the array> >int> count =>0>;> >for> (>int> i =>0>; i // remember to use jagged[i].length instead of // jagged[0].length, since every row has // different number of columns for (int j = 0; j jagged[i][j] = count++; } } // printing the values of 2D Jagged array System.out.println('The values of 2D jagged array'); for (int i = 0; i for (int j = 0; j System.out.printf(jagged[i][j] + ' '); System.out.println(); } } }> |
>
>出力
The values of 2D jagged array 0 1 2 3 4 5>
2 つの 2D 配列を追加するプログラム:
ジャワ
import> java.io.*;> import> java.util.*;> > class> GFG {> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >int>[][] arr1 = { {>1>,>2>,>3> }, {>4>,>5>,>6> } };> >int>[][] arr2 = { {>4>,>5>,>6> }, {>1>,>3>,>2> } };> >int>[][] sum =>new> int>[>2>][>3>];> > >// adding two 2D arrays element-wise> >for> (>int> i =>0>; i for (int j = 0; j 0].length; j++) { sum[i][j] = arr1[i][j] + arr2[i][j]; } } System.out.println('Resultant 2D array: '); for (int i = 0; i System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sum[i])); } } }> |
>
k 最近傍アルゴリズム
>出力
Resultant 2D array: [5, 7, 9] [5, 8, 8]>
