入力 n に対するオイラーのトーティエント関数 Φ(n) は、{1, 2, 3, …, n-1} 内の n と互いに素な数値、つまり n との GCD (最大公約数) が一致する数値の数です。は1です。
例:
Φ(1) = 1
gcd(1, 1) は 1
Φ(2) = 1
gcd(1, 2) は 1 ですが、gcd(2, 2) は 2 です。
Φ(3) = 2
gcd(1, 3) は 1、gcd(2, 3) は 1
Φ(4) = 2
gcd(1, 4) は 1、gcd(3, 4) は 1
Φ(5) = 4
gcd(1, 5) は 1、gcd(2, 5) は 1、
gcd(3, 5) は 1、gcd(4, 5) は 1
Φ(6) = 2
gcd(1, 6) は 1、gcd(5, 6) は 1、
おすすめの練習方法 オイラー トーティエント関数 試してみましょう!
入力 n の Φ(n) を計算するにはどうすればよいですか?
あ 簡単な解決策 1 から n-1 までのすべての数値を反復処理し、n を 1 として gcd で数値をカウントします。以下は、入力整数 n に対してオイラーのトーティエント関数を計算する簡単なメソッドの実装です。
階乗JavaC
// A simple C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>ジャワ // A simple java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by sunnusingh>Python3 # A simple Python3 program # to calculate Euler's # Totient Function # Function to return # gcd of a and b def gcd(a, b): if (a == 0): return b return gcd(b % a, a) # A simple method to evaluate # Euler Totient Function def phi(n): result = 1 for i in range(2, n): if (gcd(i, n) == 1): result+=1 return result # Driver Code for n in range(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') = ', phi(n), sep = '') # This code is contributed # by Smitha>C# // A simple C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void Main() { for (int n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal>JavaScript >>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd($a, $b) { if ($a == 0) return $b; return gcd($b % $a, $a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function function phi($n) { $result = 1; for ($i = 2; $i <$n; $i++) if (gcd($i, $n) == 1) $result++; return $result; } // Driver Code for ($n = 1; $n <= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>>>C++ // A simple C++ program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function #include using namespace std; // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) cout << 'phi('< 出力
ファイ(1) = 1 ファイ(2) = 1 ファイ(3) = 2 ファイ(4) = 2 ファイ(5) = 4 ファイ(6) = 2 ファイ(7) = 6 ファイ(8) = 4 ファイ( 9) = 6 ファイ(10) = 4
上記のコードは gcd 関数を O(n) 回呼び出します。 gcd 関数の時間計算量は O(h) です。ここで、h は、指定された 2 つの数値のうち小さい方の桁数です。したがって、上限は、 時間の複雑さ 上記の解の式は O(N^2 log N) [最大で Φ はどのようになりますか?101 から n までのすべての数字の n 桁]
補助スペース: O(log N)
以下は、 より良いソリューション 。このアイデアは、全関数の値が n の積全体の素因数 p を下回るというオイラーの積公式に基づいています。
この式は基本的に、Φ(n) の値が、n のすべての素因数 p について (1 – 1/p) の副積を乗算した値に等しいことを示しています。たとえば、Φ(6) の値は = 6 * (1-1/2) * (1 – 1/3) = 2 となります。
で使用されたアイデアを使用して、すべての素因数を見つけることができます。 これ 役職。
1) 初期化: 結果 = n
2) 'p' = 2 から sqrt(n) までのループを実行し、すべての 'p' に対して以下を実行します。
a) p が n を割る場合、
設定: 結果 = 結果 * (1.0 - (1.0 / (浮動小数点) p));
すべての p を n で割ります。
3) 結果を返す
以下はオイラーの積公式の実装です。
// C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function using Euler's // product formula #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and for every prime factor p, // multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) 結果 -= 結果 / n; //集合 {1,2,....,n-1} 内では、すべての数値は n と互いに素です //n が素数の場合 return (int)result; } // ドライバーコード int main() { int n; for(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) <C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula #include int phi(int n) { float result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) 結果 -= 結果 / n; //集合 {1,2,....,n-1} 内では、すべての数値は n と互いに素です //n が素数の場合 return (int)result; } // 上記をテストするドライバープログラム function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>ジャワ // Java program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n and for // every prime factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) 結果 -= 結果 / n; //集合 {1,2,....,n-1} 内では、すべての数値は n と互いに素です //n が素数の場合 return (int)result; } // 上記をテストするドライバープログラム function public static void main(String args[]) { int n; for (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.>Python3 # Python 3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function # using Euler's product formula def phi(n) : result = n # Initialize result as n # Consider all prime factors # of n and for every prime # factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1 / p) p = 2 while p * p<= n : # Check if p is a prime factor. if n % p == 0 : # If yes, then update n and result while n % p == 0 : n = n // p result = result * (1.0 - (1.0 / float(p))) p = p + 1 # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most one # such prime factor) if n>1 : result -= result // n #集合 {1,2,....,n-1} 内では、すべての数値は n と互いに素です #n が素数の場合 return int(result) # Driver range(1, 11) の n について上記の関数をテストするプログラム: print('phi(', n, ') = ', phi(n)) # このコードは、 # Nikita Tiwari によって寄稿されました。>>C# // C# program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1 / p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (float)(1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) 結果 -= 結果 / n; //集合 {1,2,....,n-1} 内では、すべての数値は n と互いに素です //n が素数の場合 return (int)result; } // ドライバーコード public static void Main() { int n; for (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.>JavaScript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi(n) { // Initialize result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) 結果 -= 結果 / n; //集合 {1,2,....,n-1} 内では、すべての数値は n と互いに素です //n が素数の場合 return parseInt(result); } // ドライバー コード (let n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi($n) { // Initialize result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n /= $p; $result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / $p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $result -= $result / $n; //集合 {1,2,....,n-1} 内では、すべての数値は n と互いに素です //n が素数の場合 return intval($result); } // ドライバー コード ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>>> 出力
ファイ(1) = 1 ファイ(2) = 1 ファイ(3) = 2 ファイ(4) = 2 ファイ(5) = 4 ファイ(6) = 2 ファイ(7) = 6 ファイ(8) = 4 ファイ( 9) = 6 ファイ(10) = 4
時間計算量: O(Φ n log n)
補助スペース: ○(1)
上記の方法では浮動小数点計算を回避できます。アイデアは、すべての素因数とその倍数を数え、この数を n から減算して全体関数の値を取得することです (素因数と素因数の倍数の gcd は 1 になりません)。
1) 結果を n として初期化します
2) すべての数値「p」を考慮します (「p」は 2 から Φ(n) まで変化します)。
p が n を割る場合、次のようにします。
a) 1 から n まで p のすべての倍数を引きます [p のすべての倍数]
n では gcd が 1 より大きい (少なくとも p) になります]
b) n を p で繰り返し除算して更新します。
3) 削減された n が 1 より大きい場合、すべての倍数を削除します。
結果からの n の。
以下は、上記のアルゴリズムの実装です。
C++ // C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and subtract their multiples // from result for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) 結果 -= 結果 / n; 結果を返します。 } // ドライバーコード int main() { int n; for(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) << endl; } return 0; } // This code is contributed by koulick_sadhu>C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include int phi(int n) { int result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) 結果 -= 結果 / n; 結果を返します。 } // 上記をテストするドライバープログラム function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>ジャワ // Java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) 結果 -= 結果 / n; 結果を返します。 } // ドライバーコード public static void main (String[] args) { int n; for (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by ajit>Python3 # Python3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function def phi(n): # Initialize result as n result = n; # Consider all prime factors # of n and subtract their # multiples from result p = 2; while(p * p <= n): # Check if p is a # prime factor. if (n % p == 0): # If yes, then # update n and result while (n % p == 0): n = int(n / p); result -= int(result / p); p += 1; # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most # one such prime factor) if (n>1): 結果 -= int(結果 / n);結果を返します。 # range(1, 11) の n のドライバー コード: print('phi(',n,') =', phi(n)); # このコードは # mits によって提供されています>>C# // C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and // subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) 結果 -= 結果 / n;結果を返します。 } // ドライバーコード static public void Main () { int n; for (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed // by akt_mit>JavaScript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi(n) { // Initialize // result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while (n % p == 0) n = parseInt(n / p); result -= parseInt(result / p); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) 結果 -= parseInt(結果 / n); 結果を返します。 } // ドライバー コード (let n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed // by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi($n) { // Initialize // result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n = (int)$n / $p; $result -= (int)$result / $p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $result -= (int)$result / $n; $result を返します。 } // ドライバー コード ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(', $n,') =', phi($n), '
'; // This code is contributed // by ajit Φ>>> 出力
ファイ(1) = 1 ファイ(2) = 1 ファイ(3) = 2 ファイ(4) = 2 ファイ(5) = 4 ファイ(6) = 2 ファイ(7) = 6 ファイ(8) = 4 ファイ( 9) = 6 ファイ(10) = 4
時間計算量: O(Φ n log n)
補助スペース: ○(1)
上記のアルゴリズムを理解するために例を見てみましょう。
n = 10。
初期化: 結果 = 10
2 は素因数であるため、n = n/i = 5、結果 = 5
3は素因数ではありません。
4*4 は以下ではないため、for ループは 3 の後に停止します。
10まで。
for ループの後、結果 = 5、n = 5
n> 1 なので、結果 = 結果 - 結果/n = 4
オイラーのトーティエント関数の興味深い性質
1) のために 素数 p 、
証拠 :
例:
2) のために 2 つの素数 a と b
証拠 :
例:
3) のために 素数 p 、
証拠 :
例:
文字列から文字へのJava
4) のために 2つの数字aとb
特殊な場合: gcd(a, b) = 1
例:
特別なケース :
5) n のすべての約数の合計関数の値の合計は n に等しくなります。
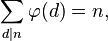
例:
n = 6
因数 = {1, 2, 3, 6}
n =
6) 最も有名で重要な機能は次のように表されます。 オイラーの定理 :
10mlをオンスに換算
定理では、n と a が互いに素である場合、
(または比較的素な) 正の整数、その後
あるΦ(n)Φ 1 (mod n)
の RSA暗号システム は次の定理に基づいています。
m が素数、つまり p である特別な場合、オイラーの定理はいわゆる次のようになります。 フェルマーの小定理 :
あるp-1Φ1(対p)
7) 法 n の加算における有限巡回群の生成器の数は Φ(n) です 。
関連記事:
n 以下のすべての数値に対するオイラーのトーティエント関数
複数の評価用に最適化されたオイラートーティエント関数
参考文献:
http://e-maxx.ru/algo/euler_function
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler%27s_totient_function
https://cp-algorithms.com/algebra/phi-function.html
http://mathcenter.oxford.memory.edu/site/math125/chineseRemainderTheorem/
