式ツリーは、さまざまな式を表現するために使用されるツリーです。ツリー データ構造は、式ステートメントを表すために使用されます。このツリーでは、内部ノードは常に演算子を表します。
- リーフ ノードは常にオペランドを表します。
- 演算は常にこれらのオペランドに対して実行されます。
- ツリーの深さに存在する演算子が常に最高の優先順位になります。
- ツリーの深さはそれほど高くないオペレーターは、深さにあるオペレーターと比較して常に最も低い優先順位になります。
- オペランドは常にツリーの深さに存在します。したがって、それは 最優先 すべてのオペレーターの中で。
- つまり、ツリーの最深部に存在する値が、ツリーの最上位に存在する他の演算子と比較して最も高い優先順位を持っていると要約できます。
- これらの式ツリーの主な用途は次のとおりです。 評価する、分析する そして 修正する いろいろな表現。
- また、式内の各演算子の結合性を調べるためにも使用されます。
- たとえば、+ 演算子は左結合であり、/ は右結合です。
- この結合性のジレンマは、式ツリーを使用することで解決されました。
- これらの式ツリーは、文脈自由文法を使用して形成されます。
- 各文法生成の前に文脈自由文法のルールを関連付けました。
- これらのルールはセマンティック ルールとも呼ばれ、これらのセマンティック ルールを使用することで、式ツリーを簡単に構築できます。
- これはコンパイラー設計の主要部分の 1 つであり、セマンティック分析フェーズに属します。
- このセマンティック分析では、構文指向の変換を使用し、出力の形式で、注釈付きの解析ツリーを生成します。
- 注釈付きの解析ツリーは、type 属性と各生成ルールに関連付けられた単純な解析に他なりません。
- 式ツリーを使用する主な目的は、複雑な式を作成することであり、これらの式ツリーを使用して簡単に評価できます。
- これは不変であり、一度作成した式ツリーを変更したり、さらに修正したりすることはできません。
- さらに変更を加えるには、新しい式ツリー全体を構築する必要があります。
- また、後置、接頭辞、および中置の式の評価を解決するためにも使用されます。
式ツリーは、 言語レベル データ形式のコード。主にツリー状構造に保存されます。のメモリ表現にも使用されます。 ラムダ 表現。ツリー データ構造を使用すると、ラムダ式をより透過的かつ明示的に表現できます。これは、式を簡単に評価できるように、コード セグメントをデータ セグメントに変換するために最初に作成されます。
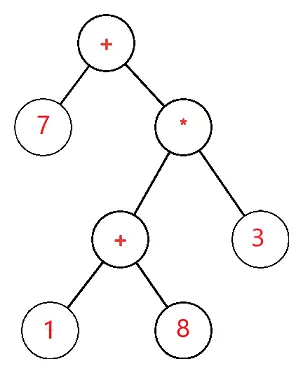
式ツリーはバイナリ ツリーで、各外部ノードまたはリーフ ノードがオペランドに対応し、各内部ノードまたは親ノードが演算子に対応するため、たとえば 7 + ((1+8)*3) の式ツリーは次のようになります。
S を式ツリーとします
S が null でない場合、
S.value がオペランドの場合、
S 値を返す
x = 解決(S.left)
y = 解決(S.right)
計算(x, y, S.value)を返します。
上記の例では、式ツリーで文脈自由文法が使用されています。
この文法には、主にとして知られるいくつかの生成ルールに関連付けられたいくつかの生成があります。 セマンティックルール 。これらの意味規則を使用して、対応する生成規則から結果生成を定義できます。ここでは、結果を計算して文法の開始記号に返す value パラメーターを使用しています。 S.left はノードの左側の子を計算します。同様に、ノードの右側の子は S.right パラメーターを使用して計算できます。
式ツリーの使用
- 式ツリーを使用する主な目的は、複雑な式を作成することであり、これらの式ツリーを使用して簡単に評価できます。
- また、式内の各演算子の結合性を調べるためにも使用されます。
- また、後置、接頭辞、および中置の式の評価を解決するためにも使用されます。
式ツリーの実装
式ツリーを実装してそのプログラムを作成するには、スタック データ構造を使用する必要があります。
スタックが後入れ先出し LIFO 原則に基づいていることがわかっているため、最近スタックにプッシュされたデータ要素は、必要なときにいつでもポップアウトされます。その実装には、スタックの主要な 2 つの操作、プッシュとポップが使用されます。プッシュ操作を使用してデータ要素をスタックにプッシュし、ポップ操作を使用してスタックからデータ要素を削除します。
式ツリー実装におけるスタックの主な機能:
まず、指定された式を左から右にスキャンして、識別された文字を 1 つずつチェックします。
- スキャンされた文字がオペランドの場合、プッシュ操作を適用してスタックにプッシュします。
- スキャンされた文字が演算子の場合、ポップ操作を適用してスタックから 2 つの値を削除してその子にし、その後、現在の親ノードをスタックにプッシュバックします。
C プログラミング言語での式ツリーの実装
// C program for expression tree implementation #include #include /* The below structure node is defined as a node of a binary tree consists of left child and the right child, along with the pointer next which points to the next node */ struct node { char info ; struct node* l ; struct node* r ; struct node* nxt ; }; struct node *head=NULL; /* Helper function that allocates a new node with the given data and NULL left and right pointers. */ struct node* newnode(char data) { struct node* node = (struct node*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct node ) ) ; node->info = data ; node->l = NULL ; node->r = NULL ; node->nxt = NULL ; return ( node ) ; } void Inorder(struct node* node) { if ( node == NULL) return ; else { /* first recur on left child */ Inorder ( node->l ) ; /* then print the data of node */ printf ( '%c ' , node->info ) ; /* now recur on right child */ Inorder ( node->r ) ; } } void push ( struct node* x ) { if ( head == NULL ) head = x ; else { ( x )->nxt = head ; head = x ; } // struct node* temp ; // while ( temp != NULL ) // { // printf ( ' %c ' , temp->info ) ; // temp = temp->nxt ; // } } struct node* pop() { // Poping out the top most [pointed with head] element struct node* n = head ; head = head->nxt ; return n ; } int main() { char t[] = { 'X' , 'Y' , 'Z' , '*' , '+' , 'W' , '/' } ; int n = sizeof(t) / sizeof(t[0]) ; int i ; struct node *p , *q , *s ; for ( i = 0 ; i <n ; i++ ) { if read character is operator then popping two other elements from stack and making a binary tree ( t[i]="=" '+' || '-' '*' ' '^' s="newnode" t [ i ] p="pop()" q="pop()" s->l = q ; s->r = p; push(s); } else { s = newnode ( t [ i ] ) ; push ( s ) ; } } printf ( ' The Inorder Traversal of Expression Tree: ' ) ; Inorder ( s ) ; return 0 ; } </n> 上記のプログラムの出力は次のとおりです。
X + Y * Z / W
C++ プログラミング言語での式ツリーの実装
// C++ program for expression tree #include using namespace std ; /* The below class node is defined as a node of a binary tree consists of left child and the right child, along with the pointer next which points to the next node */ class node { public: char info ; node* l ; node* r ; node* nxt = NULL ; node ( char c ) { this->info = c ; l = NULL ; r = NULL ; } node() { l = NULL ; r = NULL ; } friend class Stack ; friend class tree ; } ; class Stack { node* head = NULL ; public: void push ( node* ) ; node* pop() ; friend class tree ; } ; class tree { public: void inorder ( node* x ) { // cout<<'tree in inorder traversal is: '<l ) ; cout <info <r } void stack::push( node* x { if ( head="=" null we are inserting here nodes at the top of stack [following lifo principle] else x->nxt = head ; head = x ; } } node* Stack::pop() { // Poping out the top most [ pointed with head ] element node* p = head ; head = head->nxt ; return p ; } int main() { string str = 'XYZ*+W/' ; // If you wish take input from user: //cout << 'Insert Postorder Expression: ' <> s; Stack s ; tree t ; node *p, *q, *re; int n = str.length() ; for ( int i = 0 ; i <n ; i++ ) { if ( str[ i ]="=" '+' || '-' '*' ' '^') re="new" node( str[i] p="s.pop()" q="s.pop()" re->l = q ; re->r = p ; s.push(re) ; } else { re = new node( str[ i ] ) ; s.push(re) ; } } cout << ' The Inorder Traversal of Expression Tree: ' ; t.inorder(re) ; return 0 ; } </n></'tree> 上記のプログラムの出力は次のとおりです。
X + Y * Z / W
Java プログラミング言語での式ツリーの実装
// Java program for expression tree import java.util.* ; /* The below class node is defined as a node of a binary tree consists of left child and the right child, along with the pointer next which points to the next node */ class Node { char info ; Node l , r ; public Node(char data) { this.info = data ; l = null ; r = null ; } } public class Main { public static boolean isOperator ( char ch ) { if ( ch == '+' || ch == '-' || ch == '*' || ch == '/' || ch == '^' ) { return true ; } return false ; } public static Node Tree ( String postfix ) { Stack st = new Stack(); Node t1,t2,temp ; for ( int i = 0 ; i <p> <strong>The output of the above program is:</strong> </p> <pre> X + Y * Z / W </pre> <hr> 