ハッシュ マップはインデックス付きのデータ構造です。ハッシュ マップは ハッシュ関数 バケットまたはスロットの配列へのキーを使用してインデックスを計算します。その値は、対応するインデックスを持つバケットにマップされます。キーは一意であり、不変です。ハッシュ マップは、中に保管されているもののラベルが付いている引き出しがあるキャビネットと考えてください。たとえば、ユーザー情報を保存する場合、電子メールをキーとみなして、そのユーザーに対応する名、姓などの値をバケットにマッピングできます。
ハッシュ関数は、ハッシュ マップの実装の中核です。キーを受け取り、それをバケット リスト内のバケットのインデックスに変換します。理想的なハッシュでは、キーごとに異なるインデックスが生成されるはずです。ただし、衝突が発生する可能性があります。ハッシュによって既存のインデックスが得られる場合、リストを追加するか再ハッシュすることで、複数の値にバケットを使用するだけで済みます。
文字を文字列に変換する
Python では、辞書はハッシュ マップの例です。検索を最適化するためにそのようなデータ構造を構築およびカスタマイズする方法を学ぶために、ハッシュ マップの実装を最初から見ていきます。
ハッシュ マップの設計には次の機能が含まれます。
- set_val(キー, 値): キーと値のペアをハッシュ マップに挿入します。値がハッシュ マップに既に存在する場合は、値を更新します。
- get_val(キー): 指定されたキーがマップされている値を返します。このマップにキーのマッピングが含まれていない場合は、レコードが見つかりませんでした。
- delete_val(キー): ハッシュ マップにキーのマッピングが含まれている場合、特定のキーのマッピングを削除します。
以下は実装です。
Python3
class> HashTable:> ># Create empty bucket list of given size> >def> __init__(>self>, size):> >self>.size>=> size> >self>.hash_table>=> self>.create_buckets()> >def> create_buckets(>self>):> >return> [[]>for> _>in> range>(>self>.size)]> ># Insert values into hash map> >def> set_val(>self>, key, val):> > ># Get the index from the key> ># using hash function> >hashed_key>=> hash>(key)>%> self>.size> > ># Get the bucket corresponding to index> >bucket>=> self>.hash_table[hashed_key]> >found_key>=> False> >for> index, record>in> enumerate>(bucket):> >record_key, record_val>=> record> > ># check if the bucket has same key as> ># the key to be inserted> >if> record_key>=>=> key:> >found_key>=> True> >break> ># If the bucket has same key as the key to be inserted,> ># Update the key value> ># Otherwise append the new key-value pair to the bucket> >if> found_key:> >bucket[index]>=> (key, val)> >else>:> >bucket.append((key, val))> ># Return searched value with specific key> >def> get_val(>self>, key):> > ># Get the index from the key using> ># hash function> >hashed_key>=> hash>(key)>%> self>.size> > ># Get the bucket corresponding to index> >bucket>=> self>.hash_table[hashed_key]> >found_key>=> False> >for> index, record>in> enumerate>(bucket):> >record_key, record_val>=> record> > ># check if the bucket has same key as> ># the key being searched> >if> record_key>=>=> key:> >found_key>=> True> >break> ># If the bucket has same key as the key being searched,> ># Return the value found> ># Otherwise indicate there was no record found> >if> found_key:> >return> record_val> >else>:> >return> 'No record found'> ># Remove a value with specific key> >def> delete_val(>self>, key):> > ># Get the index from the key using> ># hash function> >hashed_key>=> hash>(key)>%> self>.size> > ># Get the bucket corresponding to index> >bucket>=> self>.hash_table[hashed_key]> >found_key>=> False> >for> index, record>in> enumerate>(bucket):> >record_key, record_val>=> record> > ># check if the bucket has same key as> ># the key to be deleted> >if> record_key>=>=> key:> >found_key>=> True> >break> >if> found_key:> >bucket.pop(index)> >return> ># To print the items of hash map> >def> __str__(>self>):> >return> ''.join(>str>(item)>for> item>in> self>.hash_table)> hash_table>=> HashTable(>50>)> # insert some values> hash_table.set_val(>'[email protected]'>,>'some value'>)> print>(hash_table)> print>()> hash_table.set_val(>'[email protected]'>,>'some other value'>)> print>(hash_table)> print>()> # search/access a record with key> print>(hash_table.get_val(>'[email protected]'>))> print>()> # delete or remove a value> hash_table.delete_val(>'[email protected]'>)> print>(hash_table)> |
f映画インド
>
棚の犬
>
出力:
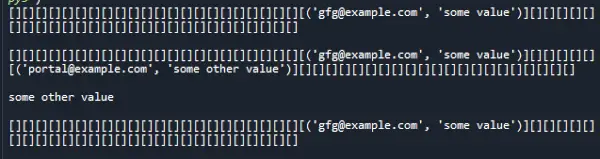
時間計算量:
メモリインデックスアクセスには一定時間がかかり、ハッシュには一定時間がかかります。したがって、ハッシュ マップの検索複雑度も定数時間、つまり O(1) になります。
ハッシュマップの利点
● ハッシュ関数による高速ランダム メモリ アクセス
Javaのデータ構造
● 負の値および非整数値を使用して値にアクセスできます。
● キーはソートされた順序で保存できるため、マップを簡単に反復できます。
ハッシュマップの欠点
● 衝突は大きなペナルティを引き起こす可能性があり、時間の複雑さが線形にまで爆発する可能性があります。
● キーの数が多い場合、単一のハッシュ関数で衝突が発生することがよくあります。
ハッシュマップの応用
LinuxでJavaのバージョンを確認する
● これらは、メモリ位置が小さなセットにマップされるキャッシュの実装に応用されます。
● データベース管理システムでタプルのインデックスを作成するために使用されます。
● これらは、Rabin Karp パターン マッチングなどのアルゴリズムでも使用されます。
