循環リンクリストとは何ですか?
の 循環リンクリスト すべてのノードが接続されて円を形成するリンク リストです。循環リンク リストでは、最初のノードと最後のノードが互いに接続されて円を形成します。最後に NULL はありません。
循環リンクリスト
循環リンク リストには通常、次の 2 種類があります。
- 循環単一リンクリスト: 循環単一リンク リストでは、リストの最後のノードには、リストの最初のノードへのポインタが含まれます。開始点と同じノードに到達するまで、循環的な単一リンク リストをたどります。循環単一リンクリストには始まりも終わりもありません。どのノードの次の部分にも null 値は存在しません。
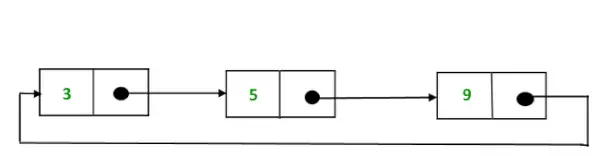
循環単一リンクリストの表現
- 循環二重リンクリスト: 循環二重リンク リストには、二重リンク リストと循環リンク リストの両方のプロパティがあり、連続する 2 つの要素が前および次のポインタによってリンクまたは接続され、最後のノードが次のポインタによって最初のノードを指し、最初のノードも次のポインタによってポイントされます。前のポインタによる最後のノード。
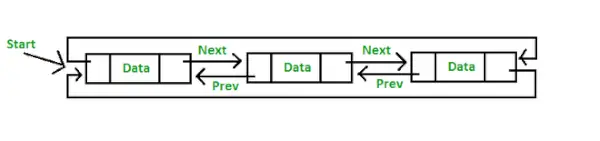
循環二重リンクリストの表現
注記: 循環リンク リストの動作を表すために、単一循環リンク リストを使用します。
循環リンクリストの表現:
循環リンク リストは、最後のノードを最初のノードに接続することを除いて、単一のリンク リストに似ています。
循環リンクリストのノード表現:
C++ // Class Node, similar to the linked list class Node{ int value; // Points to the next node. Node next; }> C struct Node { int data; struct Node *next; };> ジャワ public class Node { int data; Node next; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } }> C# public class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } }> JavaScript class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } }> PHP class Node { public $data; public $next; function __construct($data) { $this->データ = $データ; $this->next = null; } }>> Python3 # Class Node, similar to the linked list class Node: def __init__(self,data): self.data = data self.next = None>
循環単一リンクリストの例:
文字列とJava

循環リンクリストの例
上記の循環単一リンクリストは次のように表すことができます。
C++ // Initialize the Nodes. Node one = new Node(3); Node two = new Node(5); Node three = new Node(9); // Connect nodes one.next = two; two.next = three; three.next = one;>
C Node* one = createNode(3); Node* two = createNode(5); Node* three = createNode(9); // Connect nodes one->次 = 2; 2->次 = 3; 3->次 = 1;>>
ジャワ // Define the Node class class Node { int value; Node next; public Node(int value) { this.value = value; } } // Initialize the Nodes. Node one = new Node(3); Node two = new Node(5); Node three = new Node(9); // Connect nodes one.next = two; two.next = three; three.next = one;> C# Node one = new Node(3); Node two = new Node(5); Node three = new Node(9); // Connect nodes one.next = two; two.next = three; three.next = one;>
JavaScript let one = new Node(3); let two = new Node(5); let three = new Node(9); // Connect nodes one.next = two; two.next = three; three.next = one;>
PHP $one = new Node(3); $two = new Node(5); $three = new Node(9); // Connect nodes $one->次 = ; $two->next = $three; $three->next = $one;>>
Python3 # Initialize the Nodes. one = Node(3) two = Node(5) three = Node(9) # Connect nodes one.next = two two.next = three three.next = one>
説明: 上記のプログラムでは、1、2、3 はそれぞれ値 3、5、9 を持つノードで、次のように循環的に接続されています。
- ノード 1 の場合: Next ポインタには、ノード 2 のアドレスが格納されます。
- ノード 2 の場合: Next にはノード 3 のアドレスが格納されます。
- ノード 3 の場合: の 次はノード 1 を指します。
循環リンクリストの操作:
単一リンク リストと同様に、循環リンク リストに対して次のようないくつかの操作を実行できます。
- 挿入
- 削除
1. 循環リンクリストへの挿入:
ノードは次の 3 つの方法で追加できます。
JSのグローバル変数
- リストの先頭に挿入
- リストの最後に挿入
- ノード間の挿入
1) リストの先頭に挿入: リストの先頭にノードを挿入するには、次の手順に従います。
- ノードを作成します(T としましょう)。
- T -> 次 = 最後 -> 次とします。
- 最後 -> 次 = T.
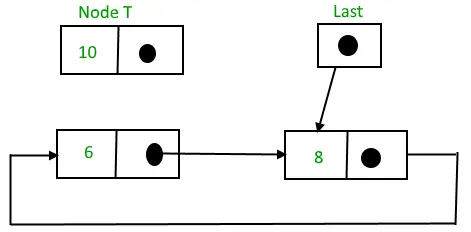
挿入前の循環リンク リスト
その後、
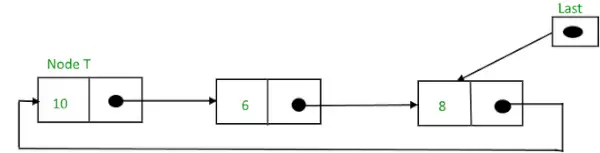
挿入後の循環リンクリスト
2) リストの最後に挿入: リストの最後にノードを挿入するには、次の手順に従います。
- ノードを作成します(T としましょう)。
- T -> next = last -> next; にします。
- 最後 -> 次 = T.
- 最後 = T.
挿入する前に、
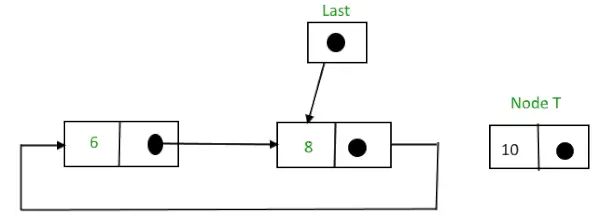
末尾にノードを挿入する前の循環リンク リスト
挿入後、
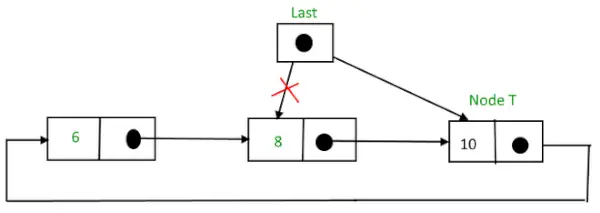
最後にノードを挿入した後の循環リンクリスト
3) ノード間の挿入: 2 つのノードの間にノードを挿入するには、次の手順に従います。
- ノードを作成します(T としましょう)。
- T を挿入する必要があるノードを検索します。そのノードが P であるとします。
- T -> 次 = P -> 次とします。
- P -> 次 = T。
ノードの値が 10 の後に 12 を挿入する必要があるとします。
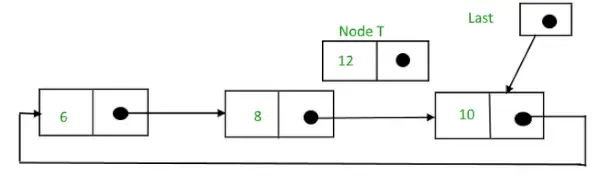
挿入前の循環リンク リスト
検索して挿入した後、
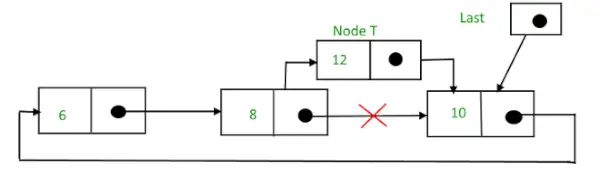
挿入後の循環リンクリスト
2. 循環リンクリスト内の削除:
1) 循環リンク リスト内の唯一のノードである場合にのみ、ノードを削除します。
データベース
- ノードのメモリを解放します
- 最後の値は NULL である必要があります。ノードは常に別のノードを指すため、NULL の割り当ては必要ありません。
任意のノードを開始点として設定できます。
ノードは最初から最後まで素早く走査されます。
2) 最後のノードの削除:
- 最後のノードの前のノードを見つけます (temp とする)
- 最後のノードの隣のノードのアドレスを一時的に保持します
- 最後の記憶を削除する
- 最後に温度を入れます
3) 循環リンク リストからノードを削除します。 ノードが与えられます。私たちのタスクは、循環リンク リストからそのノードを削除することです。
アルゴリズム:
ケース1 : リストが空です。
- リストが空の場合は、単に戻ります。
ケース2 :リストは空ではありません
- リストが空でない場合は、2 つのポインターを定義します。 カレー そして 前へ そしてポインタを初期化します カレー とともに 頭 ノード。
- 次を使用してリストを走査します カレー 削除するノードを検索し、次のノードに curr に移動する前に、毎回 prev = curr を設定します。
- ノードが見つかった場合は、それがリスト内の唯一のノードであるかどうかを確認します。 「はい」の場合は、head = NULL および free(curr) を設定します。
- リストに複数のノードがある場合は、それがリストの最初のノードであるかどうかを確認します。これをチェックする条件(curr == head)。 「はい」の場合は、最後のノードに到達するまで prev を移動します。 prev が最後のノードに到達したら、head = head -> next および prev -> next = head を設定します。カレントを削除します。
- curr が最初のノードでない場合は、それがリストの最後のノードであるかどうかを確認します。これを確認する条件は (curr -> next == head) です。
- curr が最後のノードの場合。 prev -> next = head と設定し、free(curr) でノード curr を削除します。
- 削除するノードが最初のノードでも最後のノードでもない場合は、prev -> next = curr -> next を設定し、curr を削除します。
- ノードがリストに存在しない場合は head を返し、何もしません。
上記のアプローチの実装を以下に示します。
C++ // C++ program to delete a given key from // linked list. #include using namespace std; // Structure for a node class Node { public: int data; Node* next; }; // Function to insert a node at the // beginning of a Circular linked list void push(Node** head_ref, int data) { // Create a new node and make head // as next of it. Node* ptr1 = new Node(); ptr1->データ = データ; ptr1->next = *head_ref; // リンクされたリストが NULL でない場合、 // 最後のノードの次を設定します if (*head_ref != NULL) { // ヘッドの前のノードを検索し、 // その次を更新します。 ノード* 温度 = *head_ref; while (temp->next != *head_ref) temp = temp->next; temp->next = ptr1; } else // 最初のノードの場合 ptr1->next = ptr1; *head_ref = ptr1; } // 指定された循環リンク リスト内のノードを出力する関数 // void printList(Node* head) { Node* temp = head; if (head != NULL) { do { cout<< temp->データ<< ' '; temp = temp->次; while (temp != head); }<< endl; } // Function to delete a given node // from the list void deleteNode(Node** head, int key) { // If linked list is empty if (*head == NULL) return; // If the list contains only a // single node if ((*head)->data == key && (*head)->next == *head) { free(*head); *ヘッド = NULL; 戻る; ノード *last = *head, *d; // head を削除する場合 if ((*head)->data == key) { // リストの最後のノードを検索します while (last->next != *head) last = last->next; // 最後のノードを // head の次、つまりリストの 2 番目のノードを指す // last->next = (*head)->next; フリー(*ヘッド); *head = 最後→次; 戻る; } // 削除するノードが // 見つからないか、 // リストの末尾に到達していません while (last->next != *head && last->next->data != key) { last = last ->次へ; } // 削除するノードが見つかった場合 if (last->next->data == key) { d = last->next; 最後->次 = d->次; 無料(d); それ以外の場合は<< 'Given node is not found in the list!!!
'; } // Driver code int main() { // Initialize lists as empty Node* head = NULL; // Created linked list will be // 2->5->7->8->10 Push(&head, 2); プッシュ(&head, 5); プッシュ(&ヘッド, 7); プッシュ(&head, 8); プッシュ(&head, 10); コート<< 'List Before Deletion: '; printList(head); deleteNode(&head, 7); cout << 'List After Deletion: '; printList(head); return 0; }> C #include #include // Structure for a node struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; }; // Function to insert a node at the // beginning of a Circular linked list void push(struct Node** head_ref, int data) { // Create a new node and make head // as next of it. struct Node* ptr1 = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); ptr1->データ = データ; ptr1->next = *head_ref; // リンクされたリストが NULL でない場合、 // 最後のノードの次を設定します if (*head_ref != NULL) { // ヘッドの前のノードを検索し、 // その次を更新します。 struct Node* temp = *head_ref; while (temp->next != *head_ref) temp = temp->next; temp->next = ptr1; } else // 最初のノードの場合 ptr1->next = ptr1; *head_ref = ptr1; } // 指定された循環リンク リスト内のノードを出力する関数。 // void printList(struct Node* head) { struct Node* temp = head; if (head != NULL) { do { printf('%d ', temp->data); temp = temp->next; while (temp != head); printf('
'); } // 指定されたノードをリストから削除する関数 // リストから void deleteNode(struct Node** head, int key) { // リンクされたリストが空の場合 if (*head == NULL) return; // リストにノードが 1 つしか含まれていない場合 if ((*head)->data == key && (*head)->next == *head) { free(*head); *ヘッド = NULL; 戻る; struct ノード *last = *head, *d; // head を削除する場合 if ((*head)->data == key) { // リストの最後のノードを検索します while (last->next != *head) last = last->next; // 最後のノードを // head の次、つまりリストの 2 番目のノードを指す // last->next = (*head)->next; フリー(*ヘッド); *head = 最後→次; 戻る; } // 削除するノードが // 見つからないか、 // リストの末尾に到達していません while (last->next != *head && last->next->data != key) { last = last ->次へ; } // 削除するノードが見つかった場合 if (last->next->data == key) { d = last->next; 最後->次 = d->次; 無料(d); else printf('指定されたノードがリストに見つかりません!!!
'); } // ドライバー コード int main() { // リストを空の struct として初期化 Node* head = NULL; // 作成されるリンクリストは // 2->5->7->8->10 Push(&head, 2); プッシュ(&head, 5); プッシュ(&ヘッド, 7); プッシュ(&head, 8); プッシュ(&head, 10); printf('削除前のリスト: '); printList(ヘッド); deleteNode(&head, 7); printf('削除後のリスト: '); printList(ヘッド); 0を返します。 }>> ジャワ // Java program to delete a given key from // linked list. import java.io.*; import java.util.*; public class GFG { /* structure for a node */ static class Node { int data; Node next; }; /* Function to insert a node at the beginning of a Circular linked list */ static Node push(Node head_ref, int data) { // Create a new node and make head as next // of it. Node ptr1 = new Node(); ptr1.data = data; ptr1.next = head_ref; /* If linked list is not null then set the next of last node */ if (head_ref != null) { // Find the node before head and update // next of it. Node temp = head_ref; while (temp.next != head_ref) temp = temp.next; temp.next = ptr1; } else ptr1.next = ptr1; /*For the first node */ head_ref = ptr1; return head_ref; } /* Function to print nodes in a given circular linked list */ static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; if (head != null) { do { System.out.printf('%d ', temp.data); temp = temp.next; } while (temp != head); } System.out.printf('
'); } /* Function to delete a given node from the list */ static Node deleteNode(Node head, int key) { if (head == null) return null; int flag = 0; // Find the required node Node curr = head, prev = new Node(); while (curr.data != key) { if (curr.next == head) { System.out.printf( 'Given node is not found in the list!!!
'); flag = 1; break; } prev = curr; curr = curr.next; } // Check if the element is not present in the list if (flag == 1) return head; // Check if node is only node if (curr == head && curr.next == head) { head = null; return head; } // If more than one node, check if // it is first node if (curr == head) { prev = head; while (prev.next != head) prev = prev.next; head = curr.next; prev.next = head; } // check if node is last node else if (curr.next == head) { prev.next = head; } else { prev.next = curr.next; } return head; } /* Driver code */ public static void main(String args[]) { /* Initialize lists as empty */ Node head = null; /* Created linked list will be 2.5.7.8.10 */ head = push(head, 2); head = push(head, 5); head = push(head, 7); head = push(head, 8); head = push(head, 10); System.out.printf('List Before Deletion: '); printList(head); head = deleteNode(head, 7); System.out.printf('List After Deletion: '); printList(head); } } // This code is contributed by Susobhan Akhuli> C# using System; // Structure for a node public class Node { public int data; public Node next; } // Class for Circular Linked List public class CircularLinkedList { // Function to insert a node at the // beginning of a Circular linked list public static void Push(ref Node head_ref, int data) { // Create a new node and make head // as next of it. Node ptr1 = new Node(); ptr1.data = data; ptr1.next = head_ref; // If linked list is not NULL then // set the next of last node if (head_ref != null) { // Find the node before head and // update next of it. Node temp = head_ref; while (temp.next != head_ref) temp = temp.next; temp.next = ptr1; } else // For the first node ptr1.next = ptr1; head_ref = ptr1; } // Function to print nodes in a given // circular linked list public static void PrintList(Node head) { Node temp = head; if (head != null) { do { Console.Write(temp.data + ' '); temp = temp.next; } while (temp != head); } Console.WriteLine(); } // Function to delete a given node // from the list public static void DeleteNode(ref Node head, int key) { // If linked list is empty if (head == null) return; // If the list contains only a // single node if (head.data == key && head.next == head) { head = null; return; } Node last = head, d; // If head is to be deleted if (head.data == key) { // Find the last node of the list while (last.next != head) last = last.next; // Point last node to the next of // head i.e. the second node // of the list last.next = head.next; head = last.next; return; } // Either the node to be deleted is // not found or the end of list // is not reached while (last.next != head && last.next.data != key) { last = last.next; } // If node to be deleted was found if (last.next.data == key) { d = last.next; last.next = d.next; } else Console.WriteLine( 'Given node is not found in the list!!!'); } // Driver code public static void Main() { // Initialize lists as empty Node head = null; // Created linked list will be // 2->5->7->8->10 プッシュ(参照ヘッド、2); Push(ref head, 5); Push(ref head, 7); Push(ref head, 8); Push(ref head, 10); Console.Write('削除前のリスト: '); PrintList(先頭); DeleteNode(ref head, 7); Console.Write('削除後のリスト: '); PrintList(先頭); } }>> JavaScript // Javascript program to delete a given key from linked list. // Structure for a node class Node { constructor() { this.data; this.next; } } // Function to insert a node at the // beginning of a Circular linked list function push(head, data) { // Create a new node and make head // as next of it. var ptr1 = new Node(); ptr1.data = data; ptr1.next = head; // If linked list is not NULL then // set the next of last node if (head != null) { // Find the node before head and // update next of it. let temp = head; while (temp.next != head) temp = temp.next; temp.next = ptr1; } // For the first node else ptr1.next = ptr1; head = ptr1; return head; } // Function to print nodes in a given // circular linked list function printList(head) { let tempp = head; if (head != null) { do { console.log(tempp.data); tempp = tempp.next; } while (tempp != head); } } // Function to delete a given node // from the list function deleteNode(head, key) { // If linked list is empty if (head == null) return; // If the list contains only a // single node if (head.data == key && head.next == head) { head = null; return; } let last = head; // If head is to be deleted if (head.data == key) { // Find the last node of the list while (last.next != head) last = last.next; // Point last node to the next of // head i.e. the second node // of the list last.next = head.next; head = last.next; return; } // Either the node to be deleted is // not found or the end of list // is not reached while (last.next != head && last.next.data != key) { last = last.next; } // If node to be deleted was found if (last.next.data == key) { d = last.next; last.next = d.next; d = null; } else console.log('Given node is not found in the list!!!'); } // Driver code // Initialize lists as empty head = null; // Created linked list will be // 2->5->7->8->10 ヘッド = プッシュ(ヘッド, 2); head = プッシュ(head, 5); head = プッシュ(head, 7); head = プッシュ(head, 8); head = プッシュ(head, 10); console.log('削除前のリスト: '); printList(ヘッド); deleteNode(head, 7); console.log('削除後のリスト: '); printList(ヘッド);>> Python3 # Python program to delete a given key from linked list class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None # Function to insert a node at the # beginning of a Circular linked list def push(head, data): # Create a new node and make head as next of it. newP = Node(data) newP.next = head # If linked list is not NULL then # set the next of last node if head != None: # Find the node before head and # update next of it. temp = head while (temp.next != head): temp = temp.next temp.next = newP else: newP.next = newP head = newP return head # Function to print nodes in a given circular linked list def printList(head): if head == None: print('List is Empty') return temp = head.next print(head.data, end=' ') if (head != None): while (temp != head): print(temp.data, end=' ') temp = temp.next print() # Function to delete a given node # from the list def deleteNode(head, key): # If linked list is empty if (head == None): return # If the list contains only a # single node if (head.data == key and head.next == head): head = None return last = head # If head is to be deleted if (head.data == key): # Find the last node of the list while (last.next != head): last = last.next # Point last node to the next of # head i.e. the second node # of the list last.next = head.next head = last.next return # Either the node to be deleted is # not found or the end of list # is not reached while (last.next != head and last.next.data != key): last = last.next # If node to be deleted was found if (last.next.data == key): d = last.next last.next = d.next d = None else: print('Given node is not found in the list!!!') # Driver code # Initialize lists as empty head = None # Created linked list will be # 2->5->7->8->10 ヘッド = プッシュ(ヘッド, 2) ヘッド = プッシュ(ヘッド, 5) ヘッド = プッシュ(ヘッド, 7) ヘッド = プッシュ(ヘッド, 8) ヘッド = プッシュ(ヘッド, 10) print('削除前のリスト: ') printList(head) deleteNode(head, 7) print('削除後のリスト: ') printList(head)>> 出力
List Before Deletion: 10 8 7 5 2 List After Deletion: 10 8 5 2>
時間計算量: O(N)、最悪のケースは、削除する要素が最後の要素であり、リスト全体を移動する必要がある場合に発生します。
補助スペース: O(1)、定数として余分なスペースが使用されます。
循環リンクリストの利点:
- 任意のノードを開始点にすることができます。任意の点から開始してリスト全体を調べることができます。最初に訪問したノードが再び訪問されたときに停止する必要があるだけです。
- キューの実装に役立ちます。とは異なり これ 実装では、循環リンク リストを使用する場合、前後の 2 つのポインターを維持する必要はありません。最後に挿入されたノードへのポインタを維持することができ、先頭は常に最後の次として取得できます。
- 循環リストは、リストを繰り返し巡回するアプリケーションで役立ちます。たとえば、PC 上で複数のアプリケーションが実行されている場合、オペレーティング システムは実行中のアプリケーションをリストに登録して順番に実行し、各アプリケーションに実行時間を与え、その間待機させるのが一般的です。 CPU は別のアプリケーションに割り当てられます。オペレーティング システムが循環リストを使用すると、リストの最後に到達したときにリストの先頭に循環できるので便利です。
- 循環二重リンクリストは、次のような高度なデータ構造の実装に使用されます。 フィボナッチヒープ 。
- 循環リンク リストの実装は、ツリーやグラフなどの他の複雑なデータ構造に比べて比較的簡単です。
循環リンクリストの欠点:
- 単一リンクリストと比較して、循環リストはより複雑です。
- 循環リストを反転することは、循環リストを 1 つまたは 2 つ反転することよりも複雑です。
- コードを注意深く扱わないと、コードが無限ループに陥る可能性があります。
- リストの終わりを見つけてループを制御するのが難しくなります。
- 循環リンク リストは特定のアプリケーションでは効率的ですが、リストの並べ替えや検索が必要な場合など、特定の場合には他のデータ構造よりもパフォーマンスが低下する可能性があります。
- 循環リンク リストは個々のノードへの直接アクセスを提供しません
循環リンクリストの応用:
- マルチプレイヤー ゲームはこれを使用して、各プレイヤーにプレイの機会を与えます。
- 循環リンク リストを使用すると、オペレーティング システム上で実行中の複数のアプリケーションを整理できます。これらのアプリケーションは OS によって反復処理されます。
- 循環リンク リストは、リソース割り当て問題で使用できます。
- 循環リンク リストは循環バッファを実装するためによく使用されます。
- 循環リンク リストは、シミュレーションやゲームで使用できます。
なぜ循環リンクリストなのでしょうか?
- ノードは常に別のノードを指すため、NULL 割り当ては必要ありません。
- 任意のノードを開始点として設定できます。
- ノードは最初から最後まで素早く走査されます。
次の投稿: 循環リンクリスト |セット 2 (トラバーサル) 円形の単一リンクリスト |挿入 上記のコード/アルゴリズムにバグを見つけた場合、または同じ問題を解決する他の方法を見つけた場合は、コメントを書いてください。
