あ C++ 優先キュー これはコンテナアダプタの一種であり、キューの最初の要素がキュー内のすべての要素の中で最大または最小になるように特別に設計されており、要素は非増加または非減少の順序になります(したがって、それぞれがキューの要素の優先順位は {固定順序}) です。
C++ STL では、デフォルトでは常に先頭の要素が最大になります。上部の最小要素に変更することもできます。優先キューは最大ヒープの最上部に構築され、内部構造として配列またはベクトルを使用します。簡単な言葉で、 STL プライオリティ キュー C++の実装です
数学クラスJava
// C++ program to demonstrate the use of priority_queue> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // driver code> int> main()> {> >int> arr[6] = { 10, 2, 4, 8, 6, 9 };> >// defining priority queue> >priority_queue<>int>>pq;>> >// printing array> >cout <<>'Array: '>;> >for> (>auto> i : arr) {> >cout << i <<>' '>;> >}> >cout << endl;> >// pushing array sequentially one by one> >for> (>int> i = 0; i <6; i++) {> >pq.push(arr[i]);> >}> >// printing priority queue> >cout <<>'Priority Queue: '>;> >while> (!pq.empty()) {> >cout << pq.top() <<>' '>;> >pq.pop();> >}> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>出力
Array: 10 2 4 8 6 9 Priority Queue: 10 9 8 6 4 2>
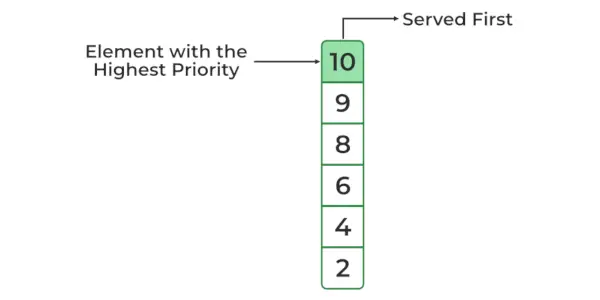
最大ヒープ優先キュー (デフォルトのスキーム)
優先キューの最小ヒープを作成するにはどうすればよいですか?
前に見たように、C++ ではプライオリティ キューはデフォルトで最大ヒープとして実装されますが、プライオリティ キューの作成時に別のパラメータを渡すことで、それを最小ヒープに変更するオプションも提供されます。
構文:
priority_queue gq;>
どこ、
- 「int」は、優先キューに格納する要素のタイプです。この場合、それは整数です。交換できます 整数 必要な他のデータ型も使用できます。 「vector」は、これらの要素を格納するために使用される内部コンテナのタイプです。 std::priority_queue それ自体はコンテナーではなく、コンテナーアダプターです。他の容器を包みます。この例では、 ベクター ただし、front()、push_back()、pop_back() メソッドをサポートする別のコンテナを選択することもできます。
- ' より大きな ' はカスタム比較関数です。これにより、優先キュー内で要素がどのように順序付けされるかが決まります。この特定の例では、greater が 最小ヒープ 。これは、最小の要素がキューの先頭になることを意味します。
最大ヒープの場合、これらのデフォルト値はすでに最大ヒープに適しているため、それらを指定する必要はありませんでした。
例:
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate> // min heap for priority queue> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> void> showpq(> >priority_queue<>int>, vector<>int>>、より大きい<>int>>> g)>> {> >while> (!g.empty()) {> >cout <<>' '> << g.top();> >g.pop();> >}> >cout <<>'
'>;> }> void> showArray(>int>* arr,>int> n)> {> >for> (>int> i = 0; i cout << arr[i] << ' '; } cout << endl; } // Driver Code int main() { int arr[6] = { 10, 2, 4, 8, 6, 9 }; priority_queue |
>
>出力
Array: 10 2 4 8 6 9 Priority Queue : 2 4 6 8 9 10>
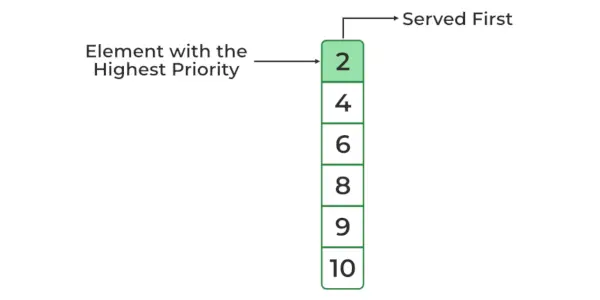
最小ヒープ優先キュー
注記: 上記の構文は覚えにくいかもしれないので、数値の場合は、値に -1 を乗算し、最大ヒープを使用して最小ヒープの効果を得ることができます。置き換えることでカスタムの並べ替え方法を使用できるだけでなく、 より大きな カスタムコンパレータ機能付き。
プライオリティキューの方式
以下の std::priority_queue クラスのすべてのメソッドのリスト:
| 方法 | 意味 |
|---|---|
| priority_queue::empty() | キューが空かどうかを返します。 |
| priority_queue::size() | キューのサイズを返します。 |
| priority_queue::top() | キューの最上位要素への参照を返します。 |
| priority_queue::push() | 要素「g」をキューの最後に追加します。 |
| priority_queue::pop() | キューの最初の要素を削除します。 |
| priority_queue::swap() | サイズが異なる場合でも、キューが同じタイプである必要がある場合に、2 つのキューの内容を交換するために使用されます。 |
| priority_queue::emplace() | 新しい要素を優先キュー コンテナに挿入するために使用されます。 |
| 優先キューの値の種類 | priority_queue の要素として格納されているオブジェクトのタイプを表します。これは、テンプレート パラメーターの同義語として機能します。 |
C++ での優先キューの操作
1. 優先キューの要素の挿入と削除
の 押す() メソッドは、要素を優先キューに挿入するために使用されます。優先キューから要素を削除するには、 ポップ() これにより、最も優先度の高い要素が削除されるため、このメソッドが使用されます。
以下は、優先キュー内のさまざまな関数の C++ プログラムです。
C++
// C++ Program to demonstrate various> // method/function in Priority Queue> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Implementation of priority queue> void> showpq(priority_queue<>int>>gq)>> {> >priority_queue<>int>>g = gq;>> (!g.empty()) {> >cout <<>' '> << g.top();> >g.pop();> >}> >cout <<>'
'>;> }> // Driver Code> int> main()> {> >priority_queue<>int>>クイズ;>> >gquiz.push(10);> >gquiz.push(30);> >gquiz.push(20);> >gquiz.push(5);> >gquiz.push(1);> >cout <<>'The priority queue gquiz is : '>;> > >// used for highlighting the element> >showpq(gquiz);> >// used for identifying the size> >// of the priority queue> >cout <<>'
gquiz.size() : '> <<> >gquiz.size();> >// used for telling the top element> >// in priority queue> >cout <<>'
gquiz.top() : '> <<> >gquiz.top();> >// used for popping the element> >// from a priority queue> >cout <<>'
gquiz.pop() : '>;> >gquiz.pop();> >showpq(gquiz);> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>出力
The priority queue gquiz is : 30 20 10 5 1 gquiz.size() : 5 gquiz.top() : 30 gquiz.pop() : 20 10 5 1>
複雑さの分析については終わりを参照してください。
注記 : 上記は、優先キューの初期化方法の 1 つです。優先キューの効率的な初期化について詳しくは、ここをクリックしてください。
2. 優先キューの最上位要素にアクセスするには
優先キューの最上位要素には、次のコマンドを使用してアクセスできます。 上() 方法。
C++
// C++ program to access the top> // element of priority queue> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >// create a priority queue of int> >priority_queue<>int>>数字;>> >numbers.push(1);> >numbers.push(20);> >numbers.push(7);> >// get the element at the top> >cout <<>'Top element: '> <<> >numbers.top();> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>出力
Top element: 20>
複雑さの分析については終わりを参照してください。
注記: 優先キューの最上位の要素にのみアクセスできます。
3. 優先キューが空かどうかを確認するには:
empty() メソッドを使用して、priority_queue が空かどうかを確認します。このメソッドは以下を返します:
- True – 優先キューが空の場合に返され、1 で表されます。 False – 優先キューが空または False ではない場合に生成され、0 で表されます。
例:
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate> // Implementation of empty() function> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >priority_queue<>int>>pqueueGFG;>>' > >// Priority Queue becomes 1> >// check if it is empty or not> >if> (pqueueGFG.empty())> >{> >cout <<>'Empty or true'>;> >}> >else> >{> >cout <<>'Contains element or False'>;> >}> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>出力
Contains element or False>
複雑さの分析については終わりを参照してください。
4. 優先キューのサイズを取得/確認するには
優先キューのサイズを決定します。簡単に言えば、 サイズ() メソッドは、内に存在する要素の数を取得するために使用されます。 優先キュー 。
以下は、優先キューのサイズを確認するための C++ プログラムです。
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the> // size() method of priority queue> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >// create a priority queue of string> >priority_queue pqueue;> >// add items to priority_queue> >pqueue.push(>'Geeks'>);> >pqueue.push(>'for'>);> >pqueue.push(>'Geeks'>);> >pqueue.push(>'C++'>);> >// get the size of queue> >int> size = pqueue.size();> >cout <<>'Size of the queue: '> << size;> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>出力
Size of the queue: 4>
複雑さの分析については終わりを参照してください。
地図Java
5. 優先キューの内容を同様のタイプの別のキューと交換するには
スワップ() この関数は、ある優先キューの内容を、同じタイプおよび同じまたは異なるサイズの別の優先キューと交換するために使用されます。
以下は、優先キューの内容を同様のタイプの別のキューと交換する C++ プログラムです。
C++
// CPP program to illustrate> // Implementation of swap() function> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Print elements of priority queue> void> print(priority_queue<>int>>pq)> {> >while> (!pq.empty()) {> >cout << pq.top() <<>' '>;> >pq.pop();> >}> >cout << endl;> }> int> main()> {> >// priority_queue container declaration> >priority_queue<>int>>pq1;>>' int>>pq2;>>' >pq1.push(1);> >pq1.push(2);> >pq1.push(3);> >pq1.push(4);> >// pushing elements into the 2nd priority queue> >pq2.push(3);> >pq2.push(5);> >pq2.push(7);> >pq2.push(9);> >cout <<>'Before swapping:-'> << endl;> >cout <<>'Priority Queue 1 = '>;> >print(pq1);> >cout <<>'Priority Queue 2 = '>;> >print(pq2);> >// using swap() function to swap elements of priority> >// queues> >pq1.swap(pq2);> >cout << endl <<>'After swapping:-'> << endl;> >cout <<>'Priority Queue 1 = '>;> >print(pq1);> >cout <<>'Priority Queue 2 = '>;> >print(pq2);> >return> 0;> }> // This code is contributed by Susobhan Akhuli> |
>
>出力
Before swapping:- Priority Queue 1 = 4 3 2 1 Priority Queue 2 = 9 7 5 3 After swapping:- Priority Queue 1 = 9 7 5 3 Priority Queue 2 = 4 3 2 1>
複雑さの分析については終わりを参照してください。
6. 新しい要素を優先キューコンテナに配置するには
埋め込む() 関数を使用して新しい要素を優先キュー コンテナに挿入すると、新しい要素はその優先順位に従って優先キューに追加されます。プッシュ操作と同様です。違いは、emplace() 操作によりオブジェクトの不要なコピーが保存されることです。
以下は、新しい要素を優先キュー コンテナーに配置する C++ プログラムです。
C++
// CPP program to illustrate> // Implementation of emplace() function> #include> using> namespace> std;> int> main()> {> >priority_queue<>int>>pq;>> >pq.emplace(1);> >pq.emplace(2);> >pq.emplace(3);> >pq.emplace(4);> >pq.emplace(5);> >pq.emplace(6);> >// Priority queue becomes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6> >// Printing the priority queue> >cout <<>'Priority Queue = '>;> >while> (!pq.empty()) {> >cout << pq.top() <<>' '>;> >pq.pop();> >}> >return> 0;> }> // This code is contributed by Susobhan Akhuli> |
>
>出力
Priority Queue = 6 5 4 3 2 1>
複雑さの分析については終わりを参照してください。
7. priority_queue の要素として格納されているオブジェクトのタイプを表すため
priority_queue :: value_type メソッドは、priority_queue の要素として格納されているオブジェクトのタイプを表す C++ STL の組み込み関数です。これは、テンプレート パラメーターの同義語として機能します。
構文:
priority_queue::value_type variable_name>
以下は、priority_queue の要素として格納されるオブジェクトのタイプを表す C++ プログラムです。
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the> // priority_queue :: value_type function> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >// declare integer value_type for priority queue> >priority_queue<>int>>::value_type AnInt;>> >// declare string value_type for priority queue> >priority_queue::value_type AString;> >// Declares priority_queues> >priority_queue<>int>>q1;>> >// Here AnInt acts as a variable of int data type> >AnInt = 20;> >cout <<>'The value_type is AnInt = '> << AnInt << endl;> >q1.push(AnInt);> >AnInt = 30;> >q1.push(AnInt);> >cout <<>'Top element of the integer priority_queue is: '> ><< q1.top() << endl;> >// here AString acts as a variable of string data type> >AString =>'geek'>;> >cout << endl> ><<>'The value_type is AString = '> << AString> ><< endl;> >q2.push(AString);> >AString =>'for'>;> >q2.push(AString);> >AString =>'geeks'>;> >q2.push(AString);> >cout <<>'Top element of the string priority_queue is: '> ><< q2.top() << endl;> >return> 0;> }> // This code is contributed by Susobhan Akhuli> |
>
>出力
The value_type is AnInt = 20 Top element of the integer priority_queue is: 30 The value_type is AString = geek Top element of the string priority_queue is: geeks>
複雑さの分析については終わりを参照してください。
すべての操作の複雑さ:
| メソッド | 時間計算量 | 補助スペース |
|---|---|---|
| priority_queue::empty() | ○(1) | ○(1) |
| priority_queue::size() | ○(1) マップJavaイテレータ | ○(1) |
| priority_queue::top() | ○(1) | ○(1) |
| priority_queue::push() | O(logN) | ○(1) |
| priority_queue::pop() | O(logN) | ○(1) |
| priority_queue::swap() | ○(1) | の上) |
| priority_queue::emplace() | O(logN) | ○(1) |
| 優先キューの値の種類 | ○(1) | ○(1) |
