意思決定は、ほぼすべてのプログラミング言語にとって最も重要な側面です。名前が示すように、意思決定では、特定の意思決定のために特定のコード ブロックを実行できます。ここでは、特定の条件の有効性について決定が行われます。状態チェックは意思決定の根幹です。
YouTubeビデオVLCをダウンロードする方法
Pythonでは以下のような文で意思決定を行います。
| 声明 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| If ステートメント | if ステートメントは、特定の条件をテストするために使用されます。条件が true の場合、コードのブロック (if ブロック) が実行されます。 |
| If - else ステートメント | if-else ステートメントは、チェックされる条件が false の場合のコード ブロックも提供するという点を除いて、if ステートメントと似ています。 if ステートメントで指定された条件が false の場合、else ステートメントが実行されます。 |
| ネストされた if ステートメント | ネストされた if ステートメントを使用すると、if ? を使用できるようになります。外側の if ステートメント内の else ステートメント。 |
Python のインデント
プログラミングを容易にし、簡潔さを実現するために、Python ではブロック レベルのコードに括弧を使用することを許可していません。 Python では、ブロックを宣言するためにインデントが使用されます。 2 つのステートメントが同じインデント レベルにある場合、それらは同じブロックの一部となります。
一般に、ステートメントをインデントするために 4 つのスペースが与えられますが、これは Python での一般的なインデント量です。
インデントはコードのブロックを宣言するため、Python 言語で最もよく使用される部分です。 1 つのブロックのすべてのステートメントは、同じレベルのインデントを対象としています。 Python での意思決定やその他の処理で実際のインデントがどのように行われるかを見ていきます。
if ステートメント
if ステートメントは特定の条件をテストするために使用され、条件が true の場合は、if ブロックとして知られるコード ブロックが実行されます。 if ステートメントの条件には、true または false に評価できる任意の有効な論理式を指定できます。
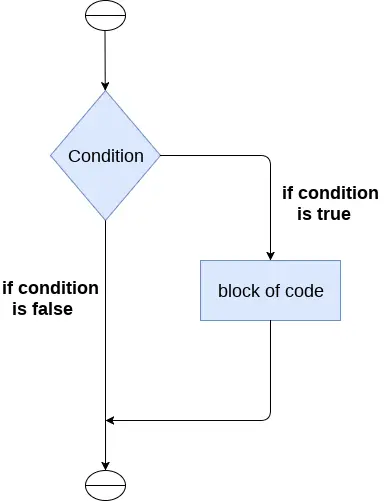
if 文の構文は次のとおりです。
if expression: statement
例1
# Simple Python program to understand the if statement num = int(input('enter the number:')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if num%2 == 0: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The Given number is an even number')
出力:
enter the number: 10 The Given number is an even number
例 2: 3 つの数値のうち最大のものを出力するプログラム。
# Simple Python Program to print the largest of the three numbers. a = int (input('Enter a: ')); b = int (input('Enter b: ')); c = int (input('Enter c: ')); if a>b and a>c: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given a is largest'); if b>a and b>c: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given b is largest'); if c>a and c>b: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given c is largest');
出力:
Enter a: 100 Enter b: 120 Enter c: 130 From the above three numbers given c is largest
if-else ステートメント
if-else ステートメントは、条件が false の場合に実行される if ステートメントと組み合わせた else ブロックを提供します。
条件が true の場合、if ブロックが実行されます。それ以外の場合は、else ブロックが実行されます。

if-else ステートメントの構文を以下に示します。
onclick js
if condition: #block of statements else: #another block of statements (else-block)
例 1 : 投票資格があるかどうかを確認するプログラム。
# Simple Python Program to check whether a person is eligible to vote or not. age = int (input('Enter your age: ')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if age>=18: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('You are eligible to vote !!'); else: print('Sorry! you have to wait !!');
出力:
Enter your age: 90 You are eligible to vote !!
例 2: 数値が偶数かどうかを確認するプログラム。
# Simple Python Program to check whether a number is even or not. num = int(input('enter the number:')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if num%2 == 0: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The Given number is an even number') else: print('The Given Number is an odd number')
出力:
enter the number: 10 The Given number is even number
エリフステートメント
elif ステートメントを使用すると、複数の条件をチェックし、その中の真の条件に応じてステートメントの特定のブロックを実行できます。必要に応じて、プログラム内に任意の数の elif ステートメントを含めることができます。ただし、elif の使用はオプションです。
elif ステートメントは、C の if-else-if ラダー ステートメントのように機能します。このステートメントの後に if ステートメントを続ける必要があります。
elif ステートメントの構文を以下に示します。
サルマン・カーンの年齢
if expression 1: # block of statements elif expression 2: # block of statements elif expression 3: # block of statements else: # block of statements

例1
# Simple Python program to understand elif statement number = int(input('Enter the number?')) # Here, we are taking an integer number and taking input dynamically if number==10: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equals to 10') elif number==50: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equal to 50'); elif number==100: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equal to 100'); else: print('The given number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100');
出力:
Enter the number?15 The given number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
例 2
# Simple Python program to understand elif statement marks = int(input('Enter the marks? ')) # Here, we are taking an integer marks and taking input dynamically if marks > 85 and marks 60 and marks 40 and marks 30 and marks <= 40): # here, we are checking the condition. if condition is true, will enter block print('you scored grade c ...') else: print('sorry you fail ?') < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Enter the marks? 89 Congrats ! you scored grade A ... </pre> <hr></=> 