ランタイムエラー:
- プログラムの実行時エラーは、プログラムが正常にコンパイルされた後、実行中に発生するエラーです。
- 実行時エラーは一般に次のように呼ばれます。 バグ ソフトウェアがリリースされる前のデバッグ プロセス中に見つかることがよくあります。
- プログラムが一般に配布された後に実行時エラーが発生した場合、開発者は多くの場合、エラーを修正するためのパッチや小さなアップデートをリリースします。
- 初心者が直面する可能性のある問題のリストを誰でも見つけることができます。 この記事 。
- オンライン プラットフォーム上で問題を解決する際、多くの実行時エラーが発生する可能性がありますが、それらのエラーは、それに伴うメッセージに明確に記載されていません。次のようなさまざまな実行時エラーが発生します。 論理エラー 、 入出力エラー 、 未定義オブジェクトエラー 、 ゼロ除算エラー 、 などなど。
ランタイムエラーの種類:
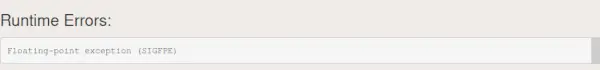
- シグペ: SIGFPE は、 浮動小数点 エラー。事実上常に原因は次のとおりです。 0による除算 。 SIGFPE エラーの原因としては、主に次の 3 つが考えられます。
- ゼロ除算。
- ゼロによるモジュロ演算。
- 整数オーバーフロー。
// C++ program to illustrate // the SIGFPE error #include using namespace std; // Driver Code int main() { int a = 5; // Division by Zero cout << a / 0; return 0; }>public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 5; try { // Division by Zero System.out.println(a / 0); } catch (ArithmeticException e) { // Handle the ArithmeticException System.out.println('Error: Division by zero is not allowed.'); } } }># Python program to illustrate # the ZeroDivisionError # Driver Code def main(): a = 5 try: # Division by Zero print(a / 0) except ZeroDivisionError as e: print(f'Error: {e}') if __name__ == '__main__': main()>using System; class Program { static void Main() { int a = 5; try { // Division by Zero Console.WriteLine(a / 0); } catch (DivideByZeroException ex) { // Handling DivideByZeroException Console.WriteLine('Error: ' + ex.Message); } Console.ReadLine(); } }>// JavaScript program to demonstrate division by zero behavior // Perform division by zero let result = 5 / 0; // Print the result console.log(result);>
- シガブト: エラー自体はプログラムによって検出され、このシグナルは呼び出しを使用して生成されます。 アボート() 関数。この信号は、内部エラーを報告するために標準ライブラリでも使用されます。 主張する() で機能する C++ また、abort() を使用してこのシグナルを生成します。以下は、SIGBRT エラーを説明するプログラムです。C++
// C++ program to illustrate // the SIGBRT error #include using namespace std; // Driver Code int main() { // Assigning excessive memory int a = 100000000000; int* arr = new int[a]; return 0; }>public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { try { // Assigning excessive memory int a = 1000000000; int[] arr = new int[a]; } catch (OutOfMemoryError e) { // Catch the OutOfMemoryError System.err.println('Caught OutOfMemoryError: ' + e.getMessage()); } } } //This code is contributed by Adarsh># Python program to illustrate # the MemoryError # Driver Code def main(): try: # Attempting to allocate excessive memory a = 100000000000 arr = [0] * a except MemoryError as e: print(f'Error: {e}') if __name__ == '__main__': main()>// JavaScript program to illustrate the MemoryError // Driver Code function main() { try { // Attempting to allocate excessive memory const a = 100000000000; const arr = new Array(a).fill(0); } catch (e) { console.log('Error: ' + e.message); } } main();>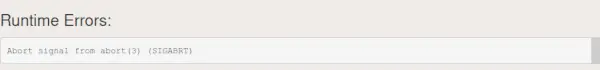
- NZEC: このエラーの意味は、 ゼロ以外の終了コード 。のために C ユーザーの場合、このエラーは次の場合に生成されます。 main() メソッド 見返りがありません 0 声明。 ジャワ /C++ ユーザーが例外をスローすると、このエラーが生成される可能性があります。 NZEC エラーが発生する考えられる理由は次のとおりです。
- 無限再帰、またはスタック メモリが不足した場合。
- 負の配列インデックスがアクセスされます。
- ArrayIndexOutOfBounds 例外。
- StringIndexOutOfBounds 例外。
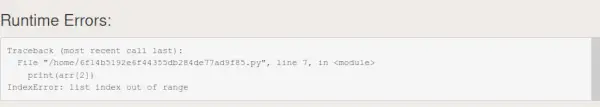
#include #include using namespace std; int main() { vectorarr = {1, 2}; try { // 意図的なエラー: 範囲外の要素にアクセスしています cout<< arr.at(2) << endl; // Accessing index 2 which is out of bounds } catch (const out_of_range& e) { cout << 'Error the index is out of bound'<< endl; // Handle the out_of_range exception } return 0; } //This code is contrbiuted by Adarsh> public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {1, 2}; // Intentional Error: Accessing an element out of bounds System.out.println(arr[2]); // Error: Accessing index 2 which is out of bounds } } //this code is contributed by Utkarsh.># Python program to illustrate # the NZEC Error # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': arr = [1, 2] # Runtime Error # Array Index out of Bounds print(arr[2])>
// JavaScript program to illustrate // the error similar to NZEC Error // Driver Code let arr = [1, 2]; // Runtime Error // Array Index out of Bounds console.log(arr[2]);>
- シグセグブ: このエラーは最も一般的なエラーであり、次のように呼ばれます。 セグメンテーション違反 。これは、プログラムがアクセスを許可されていないメモリにアクセスしようとしたり、許可されていない方法でメモリの場所にアクセスしようとしたときに生成されます。セグメンテーション違反の一般的な理由のリストは次のとおりです。
- 範囲外の配列にアクセスしています。
- NULL ポインターの逆参照。
- 解放されたメモリの逆参照。
- 初期化されていないポインタの逆参照。
- 間違った使用法 & (の住所)と * (逆参照) 演算子。
- printf および scanf ステートメント内の不適切なフォーマット指定子。
- スタックオーバーフロー。
- 読み取り専用メモリへの書き込み。
// C++ program to illustrate // the SIGSEGV error #include using namespace std; // Function with infinite // Recursion void infiniteRecur(int a) { return infiniteRecur(a); } // Driver Code int main() { // Infinite Recursion infiniteRecur(5); }>import java.util.*; public class Main { // Function with infinite Recursion static void infiniteRecur(int a) { // Recursively call the function without a base case infiniteRecur(a); } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { // Infinite Recursion infiniteRecur(5); } } //This code is contributed by Monu.># Python program to illustrate # the SIGSEGV error # Function with infinite # Recursion def infiniteRecur(a): return infiniteRecur(a) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': # Infinite Recursion infiniteRecur(5) #This code is contributed by Utkarsh.>
using System; class Program { // Function with infinite Recursion static void InfiniteRecur(int a) { // Recursively calling the function InfiniteRecur(a); } // Driver Code static void Main() { // Infinite Recursion InfiniteRecur(5); } }>// Function with infinite Recursion function infiniteRecur(a) { // Recursively call the function without a base case infiniteRecur(a); } // Infinite Recursion infiniteRecur(5); // Note: JavaScript does not have tail-call optimization, // so running this code will eventually lead to a maximum call stack size exceeded error.>
ランタイムエラーを回避する方法:
- 初期化されていない変数の使用は避けてください。これらは次のように設定できます。 0 システム上ではありますが、コーディング プラットフォーム上ではありません。
- 配列要素の出現をすべてチェックし、範囲外でないことを確認します。
- あまりにも多くのメモリを宣言しないようにしてください。質問で指定されているメモリ制限を確認してください。
- 過度な宣言は避ける スタックメモリ 。大きな配列は関数の外側でグローバルに宣言する必要があります。
- return を終了ステートメントとして使用します。
- 参照を避ける 空きメモリ または ヌルポインタ 。




