言葉 ' トライ 「」という言葉からの抜粋です。 検索 '。 Trie は、文字列のセットを格納する、ソートされたツリーベースのデータ構造です。各ノードのアルファベットの文字数と同じ数のポインタを持ちます。単語の接頭辞を利用して辞書内の単語を検索できます。たとえば、すべての文字列が文字 ' から形成されていると仮定すると、 ある ' に ' と ' 英語のアルファベットでは、各トライ ノードは最大で次の値を持つことができます。 26 ポイント。
Trie は、デジタル ツリーまたはプレフィックス ツリーとしても知られています。トライ内のノードの位置によって、そのノードが接続されているキーが決まります。
Javaデータベースjdbc
文字列のセットに対するトライのプロパティ:
- トライのルート ノードは常に null ノードを表します。
- ノードの各子はアルファベット順にソートされます。
- 各ノードには最大で次のものを含めることができます。 26 子供 (A から Z)。
- 各ノード (ルートを除く) には、アルファベット 1 文字を保存できます。
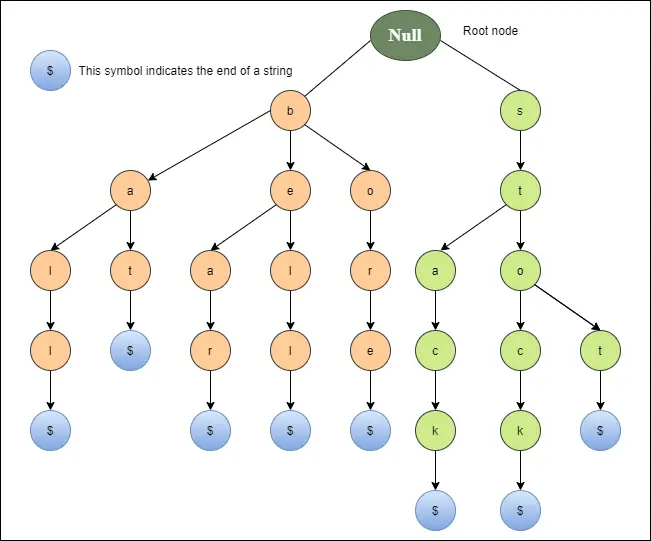
以下の図は、ベル、ベア、ボア、バット、ボール、ストップ、ストック、スタックのトライ表現を示しています。
Trieの基本操作
Trie には 3 つの操作があります。
- ノードの挿入
- ノードの検索
- ノードの削除
トライへのノードの挿入
最初の操作は、新しいノードをトライに挿入することです。実装を開始する前に、次のいくつかの点を理解することが重要です。
- 入力キー (単語) のすべての文字が個別に Trie_node に挿入されます。子は Trie ノードの次のレベルを指すことに注意してください。
- キー文字配列は子のインデックスとして機能します。
- 現在のノードがすでに現在のレターへの参照を持っている場合は、現在のノードをその参照先ノードに設定します。それ以外の場合は、新しいノードを作成し、文字を現在の文字と同じに設定し、この新しいノードで現在のノードを開始することもできます。
- 文字の長さによってトライの深さが決まります。
トライに新しいノードを挿入する実装
public class Data_Trie { private Node_Trie root; public Data_Trie(){ this.root = new Node_Trie(); } public void insert(String word){ Node_Trie current = root; int length = word.length(); for (int x = 0; x <length; x++){ char l="word.charAt(x);" node_trie node="current.getNode().get(L);" if (node="=" null){ (); current.getnode().put(l, node); } current="node;" current.setword(true); < pre> <h3>Searching a node in Trie</h3> <p>The second operation is to search for a node in a Trie. The searching operation is similar to the insertion operation. The search operation is used to search a key in the trie. The implementation of the searching operation is shown below.</p> <p>Implementation of search a node in the Trie</p> <pre> class Search_Trie { private Node_Trie Prefix_Search(String W) { Node_Trie node = R; for (int x = 0; x <w.length(); x++) { char curletter="W.charAt(x);" if (node.containskey(curletter)) node="node.get(curLetter);" } else return null; node; public boolean search(string w) node_trie !="null" && node.isend(); < pre> <h3>Deletion of a node in the Trie</h3> <p>The Third operation is the deletion of a node in the Trie. Before we begin the implementation, it is important to understand some points:</p> <ol class="points"> <li>If the key is not found in the trie, the delete operation will stop and exit it.</li> <li>If the key is found in the trie, delete it from the trie.</li> </ol> <p> <strong>Implementation of delete a node in the Trie</strong> </p> <pre> public void Node_delete(String W) { Node_delete(R, W, 0); } private boolean Node_delete(Node_Trie current, String W, int Node_index) { if (Node_index == W.length()) { if (!current.isEndOfWord()) { return false; } current.setEndOfWord(false); return current.getChildren().isEmpty(); } char A = W.charAt(Node_index); Node_Trie node = current.getChildren().get(A); if (node == null) { return false; } boolean Current_Node_Delete = Node_delete(node, W, Node_index + 1) && !node.isEndOfWord(); if (Current_Node_Delete) { current.getChildren().remove(A); return current.getChildren().isEmpty(); } return false; } </pre> <h2>Applications of Trie</h2> <p> <strong>1. Spell Checker</strong> </p> <p>Spell checking is a three-step process. First, look for that word in a dictionary, generate possible suggestions, and then sort the suggestion words with the desired word at the top.</p> <p>Trie is used to store the word in dictionaries. The spell checker can easily be applied in the most efficient way by searching for words on a data structure. Using trie not only makes it easy to see the word in the dictionary, but it is also simple to build an algorithm to include a collection of relevant words or suggestions.</p> <p> <strong>2. Auto-complete</strong> </p> <p>Auto-complete functionality is widely used on text editors, mobile applications, and the Internet. It provides a simple way to find an alternative word to complete the word for the following reasons.</p> <ul> <li>It provides an alphabetical filter of entries by the key of the node.</li> <li>We trace pointers only to get the node that represents the string entered by the user.</li> <li>As soon as you start typing, it tries to complete your input.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>3. Browser history</strong> </p> <p>It is also used to complete the URL in the browser. The browser keeps a history of the URLs of the websites you've visited.</p> <h2>Advantages of Trie</h2> <ol class="points"> <li>It can be insert faster and search the string than hash tables and binary search trees.</li> <li>It provides an alphabetical filter of entries by the key of the node.</li> </ol> <h2>Disadvantages of Trie</h2> <ol class="points"> <li>It requires more memory to store the strings.</li> <li>It is slower than the hash table.</li> </ol> <h2>Complete program in C++</h2> <pre> #include #include #include #define N 26 typedef struct TrieNode TrieNode; struct TrieNode { char info; TrieNode* child[N]; int data; }; TrieNode* trie_make(char info) { TrieNode* node = (TrieNode*) calloc (1, sizeof(TrieNode)); for (int i = 0; i <n; i++) node → child[i]="NULL;" data="0;" info="info;" return node; } void free_trienode(trienode* node) { for(int i="0;" < n; if (node !="NULL)" free_trienode(node child[i]); else continue; free(node); trie loop start trienode* trie_insert(trienode* flag, char* word) temp="flag;" for (int word[i] ; int idx="(int)" - 'a'; (temp child[idx]="=" null) child[idx]; }trie flag; search_trie(trienode* position="word[i]" child[position]="=" 0; child[position]; && 1) 1; check_divergence(trienode* len="strlen(word);" (len="=" 0) last_index="0;" len; child[position]) j="0;" <n; j++) (j child[j]) + break; last_index; find_longest_prefix(trienode* (!word || word[0]="=" '�') null; longest_prefix="(char*)" calloc 1, sizeof(char)); longest_prefix[i]="word[i];" longest_prefix[len]="�" branch_idx="check_divergence(flag," longest_prefix) (branch_idx>= 0) { longest_prefix[branch_idx] = '�'; longest_prefix = (char*) realloc (longest_prefix, (branch_idx + 1) * sizeof(char)); } return longest_prefix; } int data_node(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { TrieNode* temp = flag; for (int i = 0; word[i]; i++) { int position = (int) word[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position]) { temp = temp → child[position]; } } return temp → data; } TrieNode* trie_delete(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { if (!flag) return NULL; if (!word || word[0] == '�') return flag; if (!data_node(flag, word)) { return flag; } TrieNode* temp = flag; char* longest_prefix = find_longest_prefix(flag, word); if (longest_prefix[0] == '�') { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } int i; for (i = 0; longest_prefix[i] != '�'; i++) { int position = (int) longest_prefix[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position] != NULL) { temp = temp → child[position]; } else { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } } int len = strlen(word); for (; i <len; i++) { int position="(int)" word[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position]) trienode* rm_node="temp→child[position];" temp child[position]="NULL;" free_trienode(rm_node); } free(longest_prefix); return flag; void print_trie(trienode* flag) (!flag) return; printf('%c ', temp→info); for (int i="0;" < n; print_trie(temp child[i]); search(trienode* flag, char* word) printf('search the word %s: word); (search_trie(flag, 0) printf('not found
'); else printf('found!
'); main() flag="trie_make('�');" 'oh'); 'way'); 'bag'); 'can'); search(flag, 'ohh'); 'ways'); print_trie(flag); printf('
'); printf('deleting 'hello'...
'); 'can'...
'); free_trienode(flag); 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Search the word ohh: Not Found Search the word bag: Found! Search the word can: Found! Search the word ways: Not Found Search the word way: Found! → h → e → l → l → o → w → a → y → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'hello'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'can'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g </pre> <hr></len;></n;></pre></w.length();></pre></length;> トライの応用例
1. スペルチェッカー
スペルチェックは 3 段階のプロセスです。まず、辞書でその単語を検索し、候補を生成し、目的の単語を先頭にして候補の単語を並べ替えます。
Trie は単語を辞書に保存するために使用されます。スペル チェッカーは、データ構造上の単語を検索することにより、最も効率的な方法で簡単に適用できます。 trie を使用すると、辞書で単語を簡単に確認できるだけでなく、関連する単語や提案のコレクションを含めるアルゴリズムの構築も簡単になります。
2. オートコンプリート
辞書C#
オートコンプリート機能は、テキスト エディター、モバイル アプリケーション、インターネットで広く使用されています。これは、次の理由により、単語を完成させるための代替単語を見つける簡単な方法を提供します。
- ノードのキーによるエントリのアルファベット順のフィルターを提供します。
- ポインタをトレースするのは、ユーザーが入力した文字列を表すノードを取得するためだけです。
- 入力を開始するとすぐに、入力を完了しようとします。
3. ブラウザ履歴
ブラウザで URL を完成させるためにも使用されます。ブラウザには、アクセスした Web サイトの URL の履歴が保存されます。
トライのメリット
- ハッシュ テーブルや二分探索ツリーよりも高速に挿入して文字列を検索できます。
- ノードのキーによるエントリのアルファベット順のフィルターを提供します。
トライのデメリット
- 文字列を保存するにはより多くのメモリが必要です。
- ハッシュテーブルよりも遅いです。
C++ でプログラムを完成させる
#include #include #include #define N 26 typedef struct TrieNode TrieNode; struct TrieNode { char info; TrieNode* child[N]; int data; }; TrieNode* trie_make(char info) { TrieNode* node = (TrieNode*) calloc (1, sizeof(TrieNode)); for (int i = 0; i <n; i++) node → child[i]="NULL;" data="0;" info="info;" return node; } void free_trienode(trienode* node) { for(int i="0;" < n; if (node !="NULL)" free_trienode(node child[i]); else continue; free(node); trie loop start trienode* trie_insert(trienode* flag, char* word) temp="flag;" for (int word[i] ; int idx="(int)" - \'a\'; (temp child[idx]="=" null) child[idx]; }trie flag; search_trie(trienode* position="word[i]" child[position]="=" 0; child[position]; && 1) 1; check_divergence(trienode* len="strlen(word);" (len="=" 0) last_index="0;" len; child[position]) j="0;" <n; j++) (j child[j]) + break; last_index; find_longest_prefix(trienode* (!word || word[0]="=" \'�\') null; longest_prefix="(char*)" calloc 1, sizeof(char)); longest_prefix[i]="word[i];" longest_prefix[len]="�" branch_idx="check_divergence(flag," longest_prefix) (branch_idx>= 0) { longest_prefix[branch_idx] = '�'; longest_prefix = (char*) realloc (longest_prefix, (branch_idx + 1) * sizeof(char)); } return longest_prefix; } int data_node(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { TrieNode* temp = flag; for (int i = 0; word[i]; i++) { int position = (int) word[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position]) { temp = temp → child[position]; } } return temp → data; } TrieNode* trie_delete(TrieNode* flag, char* word) { if (!flag) return NULL; if (!word || word[0] == '�') return flag; if (!data_node(flag, word)) { return flag; } TrieNode* temp = flag; char* longest_prefix = find_longest_prefix(flag, word); if (longest_prefix[0] == '�') { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } int i; for (i = 0; longest_prefix[i] != '�'; i++) { int position = (int) longest_prefix[i] - 'a'; if (temp → child[position] != NULL) { temp = temp → child[position]; } else { free(longest_prefix); return flag; } } int len = strlen(word); for (; i <len; i++) { int position="(int)" word[i] - \'a\'; if (temp → child[position]) trienode* rm_node="temp→child[position];" temp child[position]="NULL;" free_trienode(rm_node); } free(longest_prefix); return flag; void print_trie(trienode* flag) (!flag) return; printf(\'%c \', temp→info); for (int i="0;" < n; print_trie(temp child[i]); search(trienode* flag, char* word) printf(\'search the word %s: word); (search_trie(flag, 0) printf(\'not found
\'); else printf(\'found!
\'); main() flag="trie_make('�');" \'oh\'); \'way\'); \'bag\'); \'can\'); search(flag, \'ohh\'); \'ways\'); print_trie(flag); printf(\'
\'); printf(\'deleting \'hello\'...
\'); \'can\'...
\'); free_trienode(flag); 0; pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Search the word ohh: Not Found Search the word bag: Found! Search the word can: Found! Search the word ways: Not Found Search the word way: Found! → h → e → l → l → o → w → a → y → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'hello'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g → c → a → n deleting the word 'can'... → w → a → y → h → i → t → e → a → b → a → g </pre> <hr></len;></n;> 