- RSS 形式自体は、自動プロセスでも人間でも同様に比較的簡単に読み取ることができます。
- このチュートリアルで処理される RSS は、人気のあるニュース Web サイトのトップニュース記事の RSS フィードです。チェックしてみてください ここ 。私たちの目標は、この RSS フィード (または XML ファイル) を処理し、将来使用できるように他の形式で保存することです。
#Python code to illustrate parsing of XML files # importing the required modules import csv import requests import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET def loadRSS(): # url of rss feed url = 'http://www.hindustantimes.com/rss/topnews/rssfeed.xml' # creating HTTP response object from given url resp = requests.get(url) # saving the xml file with open('topnewsfeed.xml' 'wb') as f: f.write(resp.content) def parseXML(xmlfile): # create element tree object tree = ET.parse(xmlfile) # get root element root = tree.getroot() # create empty list for news items newsitems = [] # iterate news items for item in root.findall('./channel/item'): # empty news dictionary news = {} # iterate child elements of item for child in item: # special checking for namespace object content:media if child.tag == '{https://video.search.yahoo.com/mrss': news['media'] = child.attrib['url'] else: news[child.tag] = child.text.encode('utf8') # append news dictionary to news items list newsitems.append(news) # return news items list return newsitems def savetoCSV(newsitems filename): # specifying the fields for csv file fields = ['guid' 'title' 'pubDate' 'description' 'link' 'media'] # writing to csv file with open(filename 'w') as csvfile: # creating a csv dict writer object writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile fieldnames = fields) # writing headers (field names) writer.writeheader() # writing data rows writer.writerows(newsitems) def main(): # load rss from web to update existing xml file loadRSS() # parse xml file newsitems = parseXML('topnewsfeed.xml') # store news items in a csv file savetoCSV(newsitems 'topnews.csv') if __name__ == '__main__': # calling main function main()
- 指定した URL から RSS フィードを読み込み、XML ファイルとして保存します。
- XML ファイルを解析して、各辞書が 1 つのニュース項目である辞書のリストとしてニュースを保存します。
- ニュース項目を CSV ファイルに保存します。
- 上の例で使用されているニュース Web サイトの RSS フィードをさらに見ることができます。他の RSS フィードも解析して、上記の例の拡張バージョンの作成を試みることができます。
- あなたはクリケットのファンですか?それから これ RSS フィードに興味があるはずです。この XML ファイルを解析してクリケットのライブ試合に関する情報を収集し、デスクトップ通知の作成に使用できます。
def loadRSS(): # url of rss feed url = 'http://www.hindustantimes.com/rss/topnews/rssfeed.xml' # creating HTTP response object from given url resp = requests.get(url) # saving the xml file with open('topnewsfeed.xml' 'wb') as f: f.write(resp.content) Here we first created a HTTP response object by sending an HTTP request to the URL of the RSS feed. The content of response now contains the XML file data which we save as トップニュースフィード.xml ローカルディレクトリにあります。リクエストモジュールの仕組みについて詳しくは、次の記事を参照してください。 Python を使用した GET および POST リクエスト 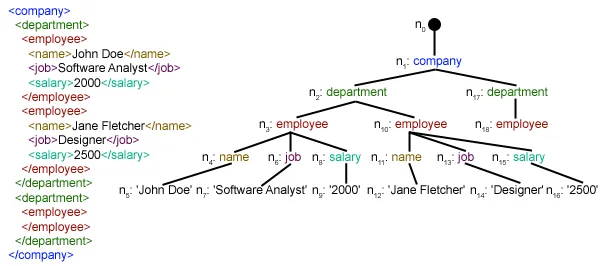 ここで私たちが使っているのは、 xml.etree.ElementTree (略してETと呼びます)モジュール。要素ツリーには、この目的のために 2 つのクラスがあります。 要素ツリー XML 文書全体をツリーとして表現し、 要素 は、このツリー内の単一のノードを表します。ドキュメント全体とのやり取り (ファイルへの読み取りとファイルへの書き込み) は通常、 要素ツリー レベル。単一の XML 要素とそのサブ要素との対話は、 要素 レベル。さて、それでは次に進みましょう parseXML() function now:
ここで私たちが使っているのは、 xml.etree.ElementTree (略してETと呼びます)モジュール。要素ツリーには、この目的のために 2 つのクラスがあります。 要素ツリー XML 文書全体をツリーとして表現し、 要素 は、このツリー内の単一のノードを表します。ドキュメント全体とのやり取り (ファイルへの読み取りとファイルへの書き込み) は通常、 要素ツリー レベル。単一の XML 要素とそのサブ要素との対話は、 要素 レベル。さて、それでは次に進みましょう parseXML() function now: tree = ET.parse(xmlfile)Here we create an 要素ツリー 渡されたオブジェクトを解析してオブジェクトを取得する xmlファイル。
root = tree.getroot()getrooted() 関数はルートを返します 木 として 要素 object.
for item in root.findall('./channel/item'): Now once you have taken a look at the structure of your XML file you will notice that we are interested only in アイテム 要素。 ./チャンネル/アイテム 実は XPath 構文 (XPath は、XML ドキュメントの一部をアドレス指定するための言語です)。ここですべてを見つけたいのです アイテム の孫たち チャネル の子供たち 根 (「.」で示される) 要素。サポートされている XPath 構文の詳細については、こちらをご覧ください。 ここ . for item in root.findall('./channel/item'): # empty news dictionary news = {} # iterate child elements of item for child in item: # special checking for namespace object content:media if child.tag == '{https://video.search.yahoo.com/mrss': news['media'] = child.attrib['url'] else: news[child.tag] = child.text.encode('utf8') # append news dictionary to news items list newsitems.append(news) Now we know that we are iterating through アイテム それぞれの要素 アイテム 要素には 1 つのニュースが含まれます。そこで、空のオブジェクトを作成します。 ニュース dictionary in which we will store all data available about news item. To iterate though each child element of an element we simply iterate through it like this: for child in item:Now notice a sample item element here:
 We will have to handle namespace tags separately as they get expanded to their original value when parsed. So we do something like this:
We will have to handle namespace tags separately as they get expanded to their original value when parsed. So we do something like this: if child.tag == '{https://video.search.yahoo.com/mrss': news['media'] = child.attrib['url'] child.attrib 要素に関連するすべての属性の辞書です。ここで私たちが興味を持っているのは、 URL の属性 メディア:コンテンツ namespace tag. Now for all other children we simply do: news[child.tag] = child.text.encode('utf8') child.tag 子要素の名前が含まれます。 子テキスト stores all the text inside that child element. So finally a sample item element is converted to a dictionary and looks like this: {'description': 'Ignis has a tough competition already from Hyun.... 'guid': 'http://www.hindustantimes.com/autos/maruti-ignis-launch.... 'link': 'http://www.hindustantimes.com/autos/maruti-ignis-launch.... 'media': 'http://www.hindustantimes.com/rf/image_size_630x354/HT/... 'pubDate': 'Thu 12 Jan 2017 12:33:04 GMT ' 'title': 'Maruti Ignis launches on Jan 13: Five cars that threa..... } Then we simply append this dict element to the list ニュース記事 。最後にこのリストが返されます。  ご覧のとおり、階層型 XML ファイル データは単純な CSV ファイルに変換され、すべてのニュース記事がテーブル形式で保存されます。これにより、データベースの拡張も容易になります。また、JSON のようなデータをアプリケーションで直接使用することもできます。これは、パブリック API は提供しないが、いくつかの RSS フィードを提供する Web サイトからデータを抽出するための最良の代替手段です。上記の記事で使用されているすべてのコードとファイルが見つかります。 ここ 。 次は何でしょうか?
ご覧のとおり、階層型 XML ファイル データは単純な CSV ファイルに変換され、すべてのニュース記事がテーブル形式で保存されます。これにより、データベースの拡張も容易になります。また、JSON のようなデータをアプリケーションで直接使用することもできます。これは、パブリック API は提供しないが、いくつかの RSS フィードを提供する Web サイトからデータを抽出するための最良の代替手段です。上記の記事で使用されているすべてのコードとファイルが見つかります。 ここ 。 次は何でしょうか? 