の フロイド・ウォーシャルアルゴリズム 、作成者の名前にちなんで名付けられました ロバート・フロイドとスティーブン・ウォーシャル 、コンピューターサイエンスとグラフ理論の基本的なアルゴリズムです。これは、重み付きグラフ内のノードのすべてのペア間の最短パスを見つけるために使用されます。このアルゴリズムは非常に効率的であり、両方のグラフを処理できます。 ポジティブ そしてn 負のエッジの重み 、幅広いネットワークおよび接続の問題を解決するための多用途ツールになります。
目次
- フロイド・ウォーシャルのアルゴリズム
- フロイド・ウォーシャル・アルゴリズムの背後にあるアイデア
- フロイド・ウォーシャルのアルゴリズム アルゴリズム
- フロイド・ウォーシャル・アルゴリズムの疑似コード
- フロイド・ウォーシャルアルゴリズムの図
- Floyd Warshall アルゴリズムの複雑さの分析
- Floyd-Warshall アルゴリズムが疎グラフではなく密グラフに適しているのはなぜですか?
- フロイド・ウォーシャルに関する重要な面接の質問
- フロイド・ウォーシャルアルゴリズムの実世界への応用
フロイド・ウォーシャルアルゴリズム:
の フロイド・ウォーシャルのアルゴリズム とは異なり、全ペア最短経路アルゴリズムです。 ディクストラ そして ベルマン・フォード これらは単一ソースの最短パス アルゴリズムです。このアルゴリズムは、 指示された そして 無向加重 グラフ。ただし、負のサイクル (サイクル内のエッジの合計が負である) を持つグラフでは機能しません。続いて 動的プログラミング すべてのノードのペア間の最短距離を計算するために、すべての可能なノードを経由するすべての可能なパスをチェックするアプローチ。
文字列を整数Javaに変換する方法
フロイド・ウォーシャル・アルゴリズムの背後にあるアイデア:
グラフがあるとします G[][] と で からの頂点 1 に N 。ここで、を評価する必要があります。 最短パスマトリックス[][] どこにある hortestPathMatrix[i][j] 頂点間の最短経路を表します 私 そして j 。
明らかに間の最短経路は、 私 に j いくつかあるでしょう k 中間ノードの数。フロイド ウォーシャル アルゴリズムの背後にある考え方は、次の各頂点を処理することです。 1 に N 中間ノードとして 1 つずつ。
次の図は、フロイド ウォーシャル アルゴリズムにおける上記の最適な部分構造プロパティを示しています。
フロイド・ウォーシャルのアルゴリズム アルゴリズム:
- 最初のステップとして、入力グラフ行列と同じソリューション行列を初期化します。
- 次に、すべての頂点を中間頂点とみなして、解行列を更新します。
- このアイデアは、すべての頂点を 1 つずつ選択し、選択した頂点を最短パスの中間頂点として含むすべての最短パスを更新することです。
- 頂点番号を選択すると k 中間頂点として、すでに頂点を考慮しています。 {0、1、2、.. k-1} 中間頂点として。
- すべてのペアについて (i、j) ソース頂点とターゲット頂点のそれぞれについて、考えられるケースは 2 つあります。
- k からの最短経路の中間頂点ではありません 私 に j 。私たちは次の価値を維持します 距離[i][j] そのまま。
- k からの最短経路の中間頂点です。 私 に j 。の値を更新します 距離[i][j] として dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]、 もし dist[i][j]> dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]
フロイド・ウォーシャル・アルゴリズムの疑似コード:>
k = 0 ~ n – 1 の場合
i = 0 ~ n – 1 の場合
j = 0 ~ n – 1 の場合
距離[i, j] = min(距離[i, j], 距離[i, k] + 距離[k, j])スクリプトを実行する方法ここで、i = 送信元ノード、j = 宛先ノード、k = 中間ノード
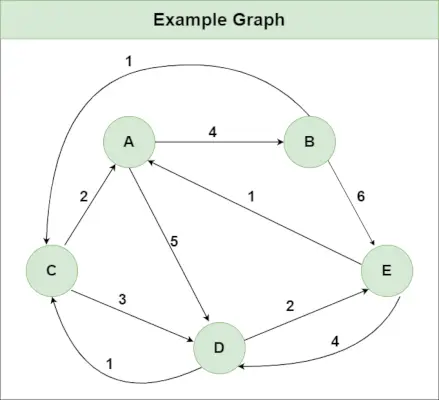
フロイド・ウォーシャル・アルゴリズムの図:
おすすめの練習方法 ぜひ試してみてください!画像に示すようなグラフがあるとします。
ステップ1 : Distance[i][j]= からのエッジの重みとなるように、入力グラフを使用して Distance[][] 行列を初期化します。 私 に j 、エッジがない場合は Distance[i][j] = Infinity ともなります。 私 に j.
ステップ2 : トリートノード あ 中間ノードとして次の式を使用して、すべての {i,j} ノード ペアの Distance[][] を計算します。
= 距離[i][j] = 最小 (距離[i][j], (i から あ ) + (からの距離 あ jへ))
= 距離[i][j] = 最小値 (距離[i][j], 距離[i][ あ ] + 距離[ あ ][j])ステップ3 : トリートノード B 中間ノードとして次の式を使用して、すべての {i,j} ノード ペアの Distance[][] を計算します。
= 距離[i][j] = 最小 (距離[i][j], (i から B ) + (からの距離 B jへ))
= 距離[i][j] = 最小値 (距離[i][j], 距離[i][ B ] + 距離[ B ][j])ゲーム鳩アンドロイドステップ4 : トリートノード C 中間ノードとして次の式を使用して、すべての {i,j} ノード ペアの Distance[][] を計算します。
= 距離[i][j] = 最小 (距離[i][j], (i から C ) + (からの距離 C jへ))
= 距離[i][j] = 最小値 (距離[i][j], 距離[i][ C ] + 距離[ C ][j])ステップ5 : トリートノード D 中間ノードとして次の式を使用して、すべての {i,j} ノード ペアの Distance[][] を計算します。
= 距離[i][j] = 最小 (距離[i][j], (i から D ) + (からの距離 D jへ))
= 距離[i][j] = 最小値 (距離[i][j], 距離[i][ D ] + 距離[ D ][j])ステップ6 : トリートノード そして 中間ノードとして次の式を使用して、すべての {i,j} ノード ペアの Distance[][] を計算します。
= 距離[i][j] = 最小 (距離[i][j], (i から そして ) + (からの距離 そして jへ))
= 距離[i][j] = 最小値 (距離[i][j], 距離[i][ そして ] + 距離[ そして ][j])ステップ7 : すべてのノードが中間ノードとして扱われたため、更新された Distance[][] 行列を応答行列として返すことができます。
果物はいくつありますか
上記のアプローチの実装を以下に示します。
C++ // C++ Program for Floyd Warshall Algorithm #include using namespace std; // Number of vertices in the graph #define V 4 /* Define Infinite as a large enough value.This value will be used for vertices not connected to each other */ #define INF 99999 // A function to print the solution matrix void printSolution(int dist[][V]); // Solves the all-pairs shortest path // problem using Floyd Warshall algorithm void floydWarshall(int dist[][V]) { int i, j, k; /* Add all vertices one by one to the set of intermediate vertices. --->反復の開始前に、すべての頂点のペア間の最短距離が得られ、その最短距離ではセット {0, 1, 2, ... k-1} 内の頂点のみが中間頂点として考慮されます。 ----> 反復終了後、頂点番号k が中間頂点のセットに追加され、そのセットは {0, 1, 2, .. k} */ for (k = 0; k< V; k++) { // Pick all vertices as source one by one for (i = 0; i < V; i++) { // Pick all vertices as destination for the // above picked source for (j = 0; j < V; j++) { // If vertex k is on the shortest path from // i to j, then update the value of // dist[i][j] if (dist[i][j]>(dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]) && (dist[k][j] != INF && dist[i][k] != INF)) dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]; } } } // 最短距離行列を出力します printSolution(dist); } /* ソリューションを出力するユーティリティ関数 */ void printSolution(int dist[][V]) { cout<< 'The following matrix shows the shortest ' 'distances' ' between every pair of vertices
'; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) { if (dist[i][j] == INF) cout << 'INF' << ' '; else cout << dist[i][j] << ' '; } cout << endl; } } // Driver's code int main() { /* Let us create the following weighted graph 10 (0)------->(3) | /| 5 | | | | 1 |/ | (1)------>(2) 3 */ intgraph[V][V] = { { 0, 5, INF, 10 }, { INF, 0, 3, INF }, { INF, INF, 0, 1 }, { INF, INF, INF, 0 } }; // 関数呼び出し floydWarshall(graph); 0を返します。 } // このコードは Mythri J L によって提供されています>>'C(3) | /| 5 | | | | 1 |/ | (1)------>(2) 3 */ intgraph[V][V] = { { 0, 5, INF, 10 }, { INF, 0, 3, INF }, { INF, INF, 0, 1 }, { INF, INF, INF, 0 } }; // 関数呼び出し floydWarshall(graph); 0を返します。 }>> ジャワ // Java program for Floyd Warshall All Pairs Shortest // Path algorithm. import java.io.*; import java.lang.*; import java.util.*; class AllPairShortestPath { final static int INF = 99999, V = 4; void floydWarshall(int dist[][]) { int i, j, k; /* Add all vertices one by one to the set of intermediate vertices. --->反復の開始前に、すべての頂点のペア間の最短距離が得られ、その最短距離ではセット {0, 1, 2, ... k-1} 内の頂点のみが中間頂点として考慮されます。 ----> 反復終了後、頂点番号k が中間頂点のセットに追加され、そのセットは {0, 1, 2, .. k} */ for (k = 0; k< V; k++) { // Pick all vertices as source one by one for (i = 0; i < V; i++) { // Pick all vertices as destination for the // above picked source for (j = 0; j < V; j++) { // If vertex k is on the shortest path // from i to j, then update the value of // dist[i][j] if (dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j]) dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]; } } } // Print the shortest distance matrix printSolution(dist); } void printSolution(int dist[][]) { System.out.println( 'The following matrix shows the shortest ' + 'distances between every pair of vertices'); for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < V; ++j) { if (dist[i][j] == INF) System.out.print('INF '); else System.out.print(dist[i][j] + ' '); } System.out.println(); } } // Driver's code public static void main(String[] args) { /* Let us create the following weighted graph 10 (0)------->(3) | /| 5 | | | | 1 |/ | (1)------>(2) 3 */ intgraph[][] = { { 0, 5, INF, 10 }, { INF, 0, 3, INF }, { INF, INF, 0, 1 }, { INF, INF, INF, 0 } }; AllPairShortestPath a = 新しい AllPairShortestPath(); // 関数呼び出し a.floydWarshall(graph); } } // Aakash Hasija による寄稿>> Python3 # Python3 Program for Floyd Warshall Algorithm # Number of vertices in the graph V = 4 # Define infinity as the large # enough value. This value will be # used for vertices not connected to each other INF = 99999 # Solves all pair shortest path # via Floyd Warshall Algorithm def floydWarshall(graph): ''' dist[][] will be the output matrix that will finally have the shortest distances between every pair of vertices ''' ''' initializing the solution matrix same as input graph matrix OR we can say that the initial values of shortest distances are based on shortest paths considering no intermediate vertices ''' dist = list(map(lambda i: list(map(lambda j: j, i)), graph)) ''' Add all vertices one by one to the set of intermediate vertices. --->反復の開始前に、すべての頂点ペア間の最短距離が得られ、その最短距離ではセット {0, 1, 2, ... k-1} 内の頂点のみが中間頂点として考慮されます。 ----> 反復終了後、頂点番号k が中間頂点のセットに追加され、そのセットは {0, 1, 2, .. k} ''' for k in range(V): # すべての頂点を i in のソースとして 1 つずつ選択しますrange(V): # すべての頂点を # 上で選択した j のソースの宛先として選択します。 range(V): # 頂点 k が # i から j への最短パス上にある場合、 # dist[i][ の値を更新します。 j] dist[i][j] = min(dist[i][j], dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] ) printSolution(dist) # 解を出力するユーティリティ関数 def printSolution (dist): print('次の行列は頂点の各ペア間の最短距離') for i in range(V): for j in range(V): if(dist[i][j] == INF): print('%7s' % ('INF'), end=' ') else: print('%7d ' % (dist[i][j]), end=' ') if j == V-1: print() # ドライバーのコード if __name__ == '__main__': ''' 10 (0)------ ->(3) | /|5| | | | 1 |/ | (1)------>(2) 3 ''' グラフ = [[0, 5, INF, 10], [INF, 0, 3, INF], [INF, INF, 0] , 1], [INF, INF, INF, 0] ] # 関数呼び出し floydWarshall(graph) # このコードは Mythri J L によって提供されています>> C# // C# program for Floyd Warshall All // Pairs Shortest Path algorithm. using System; public class AllPairShortestPath { readonly static int INF = 99999, V = 4; void floydWarshall(int[, ] graph) { int[, ] dist = new int[V, V]; int i, j, k; // Initialize the solution matrix // same as input graph matrix // Or we can say the initial // values of shortest distances // are based on shortest paths // considering no intermediate // vertex for (i = 0; i < V; i++) { for (j = 0; j < V; j++) { dist[i, j] = graph[i, j]; } } /* Add all vertices one by one to the set of intermediate vertices. --->反復の開始前に、すべての頂点のペア間の最短距離が得られ、その最短距離ではセット {0, 1, 2, ... k-1} 内の頂点のみが中間頂点として考慮されます。 ---> 反復終了後、頂点番号k が中間頂点のセットに追加され、そのセットは {0, 1, 2, .. k} */ for (k = 0; k< V; k++) { // Pick all vertices as source // one by one for (i = 0; i < V; i++) { // Pick all vertices as destination // for the above picked source for (j = 0; j < V; j++) { // If vertex k is on the shortest // path from i to j, then update // the value of dist[i][j] if (dist[i, k] + dist[k, j] < dist[i, j]) { dist[i, j] = dist[i, k] + dist[k, j]; } } } } // Print the shortest distance matrix printSolution(dist); } void printSolution(int[, ] dist) { Console.WriteLine( 'Following matrix shows the shortest ' + 'distances between every pair of vertices'); for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < V; ++j) { if (dist[i, j] == INF) { Console.Write('INF '); } else { Console.Write(dist[i, j] + ' '); } } Console.WriteLine(); } } // Driver's Code public static void Main(string[] args) { /* Let us create the following weighted graph 10 (0)------->(3) | /| 5 | | | | 1 |/ | (1)------>(2) 3 */ int[, ] グラフ = { { 0, 5, INF, 10 }, { INF, 0, 3, INF }, { INF, INF, 0 , 1 }, { INF, INF, INF, 0 } }; AllPairShortestPath a = 新しい AllPairShortestPath(); // 関数呼び出し a.floydWarshall(graph); } } // この記事は // Abdul Mateen Mohammed によって寄稿されました>> JavaScript // A JavaScript program for Floyd Warshall All // Pairs Shortest Path algorithm. var INF = 99999; class AllPairShortestPath { constructor() { this.V = 4; } floydWarshall(graph) { var dist = Array.from(Array(this.V), () =>新しい Array(this.V).fill(0)); 変数 i、j、k; // 解行列を初期化します // 入力グラフ行列と同じです // または、 // 最短距離の初期値は、 // 最短経路に基づいており、 // 中間頂点を考慮していない // (i = 0; i< this.V; i++) { for (j = 0; j < this.V; j++) { dist[i][j] = graph[i][j]; } } /* Add all vertices one by one to the set of intermediate vertices. --->反復の開始前に、すべての頂点のペア間の最短距離が得られ、その最短距離ではセット {0, 1, 2, ... k-1} 内の頂点のみが中間頂点として考慮されます。 ---> 反復終了後、頂点番号k が中間頂点のセットに追加され、そのセットは {0, 1, 2, .. k} */ for (k = 0; k< this.V; k++) { // Pick all vertices as source // one by one for (i = 0; i < this.V; i++) { // Pick all vertices as destination // for the above picked source for (j = 0; j < this.V; j++) { // If vertex k is on the shortest // path from i to j, then update // the value of dist[i][j] if (dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j]) { dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]; } } } } // Print the shortest distance matrix this.printSolution(dist); } printSolution(dist) { document.write( 'Following matrix shows the shortest ' + 'distances between every pair of vertices ' ); for (var i = 0; i < this.V; ++i) { for (var j = 0; j < this.V; ++j) { if (dist[i][j] == INF) { document.write(' INF '); } else { document.write(' ' + dist[i][j] + ' '); } } document.write(' '); } } } // Driver Code /* Let us create the following weighted graph 10 (0)------->(3) | /| 5 | | | | 1 |/ | (1)------>(2) 3 */ var chart = [ [0, 5, INF, 10], [INF, 0, 3, INF], [INF, INF, 0, 1] 、[INF、INF、INF、0]、]; var a = 新しい AllPairShortestPath(); // 解を出力します a.floydWarshall(graph); // このコードは rdtaank によって提供されています。>> PHP // PHP Program for Floyd Warshall Algorithm // Solves the all-pairs shortest path problem // using Floyd Warshall algorithm function floydWarshall ($graph, $V, $INF) { /* dist[][] will be the output matrix that will finally have the shortest distances between every pair of vertices */ $dist = array(array(0,0,0,0), array(0,0,0,0), array(0,0,0,0), array(0,0,0,0)); /* Initialize the solution matrix same as input graph matrix. Or we can say the initial values of shortest distances are based on shortest paths considering no intermediate vertex. */ for ($i = 0; $i < $V; $i++) for ($j = 0; $j < $V; $j++) $dist[$i][$j] = $graph[$i][$j]; /* Add all vertices one by one to the set of intermediate vertices. --->反復の開始前に、すべての頂点のペア間の最短距離が得られ、その最短距離ではセット {0, 1, 2, ... k-1} 内の頂点のみが中間頂点として考慮されます。 ----> 反復終了後、頂点番号k が中間頂点のセットに追加され、そのセットは {0, 1, 2, .. k} */ for ($k = 0; $k< $V; $k++) { // Pick all vertices as source one by one for ($i = 0; $i < $V; $i++) { // Pick all vertices as destination // for the above picked source for ($j = 0; $j < $V; $j++) { // If vertex k is on the shortest path from // i to j, then update the value of dist[i][j] if ($dist[$i][$k] + $dist[$k][$j] < $dist[$i][$j]) $dist[$i][$j] = $dist[$i][$k] + $dist[$k][$j]; } } } // Print the shortest distance matrix printSolution($dist, $V, $INF); } /* A utility function to print solution */ function printSolution($dist, $V, $INF) { echo 'The following matrix shows the ' . 'shortest distances between ' . 'every pair of vertices
'; for ($i = 0; $i < $V; $i++) { for ($j = 0; $j < $V; $j++) { if ($dist[$i][$j] == $INF) echo 'INF ' ; else echo $dist[$i][$j], ' '; } echo '
'; } } // Drivers' Code // Number of vertices in the graph $V = 4 ; /* Define Infinite as a large enough value. This value will be used for vertices not connected to each other */ $INF = 99999 ; /* Let us create the following weighted graph 10 (0)------->(3) | /| 5 | | | | 1 |/ | (1)------>(2) 3 */ $graph = array(array(0, 5, $INF, 10), array($INF, 0, 3, $INF), array($ INF, $INF, 0, 1), array($INF, $INF, $INF, 0)); // 関数呼び出し floydWarshall($graph, $V, $INF); // このコードは Ryuga によって提供されました ?>>> 出力
The following matrix shows the shortest distances between every pair of vertices 0 5 8 9 INF 0 3 4 INF INF 0 1 INF INF INF 0>
Floyd Warshall アルゴリズムの複雑さの分析:
- 時間計算量: O(V3)、ここで、V はグラフ内の頂点の数であり、それぞれサイズ V の 3 つのネストされたループを実行します。
- 補助スペース: O(V2)、ノードの各ペアの最短距離を保存するために 2 次元行列を作成します。
注記 : 上記のプログラムは最短距離のみを出力します。先行情報を別の 2D マトリックスに保存することによって、最短パスを出力するようにソリューションを変更することもできます。
Floyd-Warshall アルゴリズムが疎グラフではなく密グラフに適しているのはなぜですか?
密なグラフ : エッジの数が頂点の数よりも大幅に多いグラフ。
スパースグラフ : エッジの数が非常に少ないグラフ。グラフにエッジがいくつあっても、 フロイド・ウォーシャルのアルゴリズム O(V のために実行3) 回なので、次のような場合に最適です。 密なグラフ 。スパースグラフの場合、 ジョンソンのアルゴリズム の方が適しています。
フロイド=ウォーシャルに関する重要な面接の質問:
- Floyd Warshall アルゴリズムを使用してグラフ内の負のサイクルを検出するにはどうすればよいですか?
- フロイド・ウォーシャルアルゴリズムはダイクストラアルゴリズムとどう違うのですか?
- フロイド・ウォーシャル・アルゴリズムはベルマン・フォード・アルゴリズムとどう違うのですか?
フロイド・ウォーシャルアルゴリズムの実世界への応用:
- コンピュータ ネットワーキングでは、このアルゴリズムを使用して、ネットワーク内のすべてのノード ペア間の最短パスを見つけることができます。これは次のように呼ばれます ネットワークルーティング 。
- フライト接続 航空業界では、空港間の最短経路を見つけます。
- GIS ( 地理情報システム ) アプリケーションでは、場所間の最短経路を見つけるために道路網などの空間データを分析することがよくあります。
- クリーンのアルゴリズム これは floyd warshall を一般化したもので、正規言語の正規表現を見つけるために使用できます。







