Integer クラスは、プリミティブ型 int のラッパー クラスであり、int 値を文字列表現に変換したり、その逆に変換したりするなど、int 値を効果的に処理するためのメソッドがいくつか含まれています。 Integer クラスのオブジェクトは、単一の int 値を保持できます。
コンストラクター:
- 整数(int b): 指定された値で初期化された Integer オブジェクトを作成します。
構文:
Javaで文字列をintに変換する方法
public Integer(int b)>
パラメーター:
b : value with which to initialize>
- 整数(文字列): 文字列表現によって提供される int 値で初期化された Integer オブジェクトを作成します。デフォルトの基数は 10 とみなされます。
構文:
public Integer(String s) throws NumberFormatException>
パラメーター:
s : string representation of the int value>
投げる:
NumberFormatException : If the string provided does not represent any int value.>
方法:
1.toString() : int 値に対応する文字列を返します。
構文:
public String toString(int b)>
パラメーター :
b : int value for which string representation required.>
2.toHexString() : int 値に対応する文字列を 16 進数形式で返します。つまり、int 値を 16 進数文字で表す文字列 [0-9][a-f] を返します。
構文:
public String toHexString(int b)>
パラメーター:
b : int value for which hex string representation required.>
3. toOctalString() : int 値に対応する文字列を 8 進数形式で返します。つまり、int 値を 8 進数の文字 [0-7] で表す文字列を返します。
構文:
public String toOctalString(int b)>
パラメーター:
b : int value for which octal string representation required.>
4. toBinaryString() : 2 進数の int 値に対応する文字列を返します。つまり、16 進数の int 値を表す文字列 -[0/1] を返します。
構文:
public String toBinaryString(int b)>
パラメーター:
b : int value for which binary string representation required.>
5. valueOf() : 指定された値で初期化された Integer オブジェクトを返します。
構文:
public static Integer valueOf(int b)>
パラメーター:
b : a int value>
- valueOf(文字列val,int基数) : new Integer(Integer.parseInteger(val,radix)) と同様の機能を提供する別のオーバーロードされた関数
構文:
public static Integer valueOf(String val, int radix) throws NumberFormatException>
パラメーター:
val : String to be parsed into int value radix : radix to be used while parsing>
投げる:
NumberFormatException : if String cannot be parsed to a int value in given radix.>
- valueOf(文字列値) : new Integer(Integer.parseInt(val,10)) と同様の機能を提供する別のオーバーロードされた関数
構文:
public static Integer valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException>
パラメーター:
s : a String object to be parsed as int>
投げる:
NumberFormatException : if String cannot be parsed to a int value in given radix.>
6. parseInt() : 指定された基数で文字列を解析して int 値を返します。 valueOf() はプリミティブ int 値を返し、valueOf() は Integer オブジェクトを返すため、valueOf() とは異なります。
構文:
public static int parseInt(String val, int radix) throws NumberFormatException>
パラメーター:
val : String representation of int radix : radix to be used while parsing>
投げる:
NumberFormatException : if String cannot be parsed to a int value in given radix.>
- パラメーターとして String のみを含む別のオーバーロードされたメソッドでは、radix はデフォルトで 10 に設定されます。
構文:
public static int parseInt(String val) throws NumberFormatException>
パラメーター:
val : String representation of int>
投げる:
NumberFormatException : if String cannot be parsed to a int value in given radix.>
7. getInteger(): 指定されたシステム プロパティに関連付けられた値を表す Integer オブジェクトを返します。存在しない場合は null を返します。
構文:
public static Integer getInteger(String prop)>
パラメーター :
prop : System property>
- プロパティが存在しない場合、つまり null ではなく、ユーザーが指定したデフォルト値を返す、2 番目の引数を返す別のオーバーロードされたメソッドです。
構文:
public static Integer getInteger(String prop, int val)>
パラメーター:
prop : System property val : value to return if property does not exist.>
- 返された値に従って値を解析する別のオーバーロードされたメソッドです。つまり、返された値が # で始まる場合は 16 進数として解析され、0 で始まる場合は 8 進数として解析され、それ以外の場合は 10 進数として解析されます。
構文:
二分探索Python
public static Integer getInteger(String prop, Integer val)>
パラメーター:
prop : System property val : value to return if property does not exist.>
8. デコード() : 指定された文字列のデコードされた値を保持する Integer オブジェクトを返します。指定された文字列は次の形式である必要があります。それ以外の場合は NumberFormatException がスローされます。
Decimal-(符号)Decimal_Number
Hex- (符号)0xHex_Digits
Hex- (符号)0XHex_Digits
8 進数- (符号)0''Octal_Digits
構文:
public static Integer decode(String s) throws NumberFormatException>
パラメーター:
s : encoded string to be parsed into int val>
投げる:
NumberFormatException : If the string cannot be decoded into a int value>
9.rotateLeft() : 指定された値の 2 の補数形式で指定された距離だけビットを左に回転することにより、プリミティブ int を返します。左に回転すると、最上位ビットは右側、つまり最下位位置に移動します。つまり、ビットの循環移動が発生します。負の距離は右回転を意味します。
構文:
public static int rotateLeft(int val, int dist)>
パラメーター:
val : int value to be rotated dist : distance to rotate>
10.rotateRight() : 指定された値の 2 の補数形式で指定された距離だけビットを右に回転することにより、プリミティブ int を返します。右回転すると、最下位ビットが左側または最上位位置に移動します。つまり、ビットの循環移動が発生します。負の距離は左回転を意味します。
構文:
public static int rotateRight(int val, int dist)>
パラメーター:
val : int value to be rotated dist : distance to rotate>
ジャワ
// Java program to illustrate> // various Integer methods> public> class> Integer_test {> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >int> b =>55>;> >String bb =>'45'>;> >// Construct two Integer objects> >Integer x =>new> Integer(b);> >Integer y =>new> Integer(bb);> >// toString()> >System.out.println(>'toString(b) = '> >+ Integer.toString(b));> >// toHexString(),toOctalString(),toBinaryString()> >// converts into hexadecimal, octal and binary> >// forms.> >System.out.println(>'toHexString(b) ='> >+ Integer.toHexString(b));> >System.out.println(>'toOctalString(b) ='> >+ Integer.toOctalString(b));> >System.out.println(>'toBinaryString(b) ='> >+ Integer.toBinaryString(b));> >// valueOf(): return Integer object> >// an overloaded method takes radix as well.> >Integer z = Integer.valueOf(b);> >System.out.println(>'valueOf(b) = '> + z);> >z = Integer.valueOf(bb);> >System.out.println(>'ValueOf(bb) = '> + z);> >z = Integer.valueOf(bb,>6>);> >System.out.println(>'ValueOf(bb,6) = '> + z);> >// parseInt(): return primitive int value> >// an overloaded method takes radix as well> >int> zz = Integer.parseInt(bb);> >System.out.println(>'parseInt(bb) = '> + zz);> >zz = Integer.parseInt(bb,>6>);> >System.out.println(>'parseInt(bb,6) = '> + zz);> >// getInteger(): can be used to retrieve> >// int value of system property> >int> prop> >= Integer.getInteger(>'sun.arch.data.model'>);> >System.out.println(> >'getInteger(sun.arch.data.model) = '> + prop);> >System.out.println(>'getInteger(abcd) ='> >+ Integer.getInteger(>'abcd'>));> >// an overloaded getInteger() method> >// which return default value if property not found.> >System.out.println(> >'getInteger(abcd,10) ='> >+ Integer.getInteger(>'abcd'>,>10>));> >// decode() : decodes the hex,octal and decimal> >// string to corresponding int values.> >String decimal =>'45'>;> >String octal =>'005'>;> >String hex =>'0x0f'>;> >Integer dec = Integer.decode(decimal);> >System.out.println(>'decode(45) = '> + dec);> >dec = Integer.decode(octal);> >System.out.println(>'decode(005) = '> + dec);> >dec = Integer.decode(hex);> >System.out.println(>'decode(0x0f) = '> + dec);> >// rotateLeft and rotateRight can be used> >// to rotate bits by specified distance> >int> valrot =>2>;> >System.out.println(> >'rotateLeft(0000 0000 0000 0010 , 2) ='> >+ Integer.rotateLeft(valrot,>2>));> >System.out.println(> >'rotateRight(0000 0000 0000 0010,3) ='> >+ Integer.rotateRight(valrot,>3>));> >}> }> |
>
>
出力:
toString(b) = 55 toHexString(b) =37 toOctalString(b) =67 toBinaryString(b) =110111 valueOf(b) = 55 ValueOf(bb) = 45 ValueOf(bb,6) = 29 parseInt(bb) = 45 parseInt(bb,6) = 29 getInteger(sun.arch.data.model) = 64 getInteger(abcd) =null getInteger(abcd,10) =10 decode(45) = 45 decode(005) = 5 decode(0x0f) = 15 rotateLeft(0000 0000 0000 0010 , 2) =8 rotateRight(0000 0000 0000 0010,3) =1073741824>
11. byteValue() : この整数オブジェクトに対応するバイト値を返します。
構文:
public byte byteValue()>
12.shortValue() : この整数オブジェクトに対応する short 値を返します。
構文:
public short shortValue()>
13. intValue() : この Integer オブジェクトに対応する int 値を返します。
構文:
public int intValue()>
13.longValue() : この整数オブジェクトに対応するlong値を返します。
構文:
public long longValue()>
14.doubleValue() : この整数オブジェクトに対応する double 値を返します。
構文:
public double doubleValue()>
15. floatValue() : この整数オブジェクトに対応する浮動小数点値を返します。
構文:
public float floatValue()>
16.ハッシュコード() : この整数オブジェクトに対応するハッシュコードを返します。
構文:
public int hashCode()>
17. ビットカウント() : 指定された整数の 2 の補数で設定ビット数を返します。
構文:
public static int bitCount(int i)>
パラメーター:
i : int value whose set bits to count>
18.numberOfLeadingZeroes() : 値の 2 の補数形式で最上位の 1 ビットに先行する 0 ビットの数を返します。つまり、2 の補数形式の数値が 0000 1010 0000 0000 の場合、この関数は 4 を返します。
構文:
public static int numberofLeadingZeroes(int i)>
パラメーター:
i : int value whose leading zeroes to count in twos complement form>
19.numberOfTrailingZeroes() : 値の最後の 1 ビットに続く 0 ビットの数を 2 の補数形式で返します。つまり、2 の補数形式の数値が 0000 1010 0000 0000 の場合、この関数は 9 を返します。
構文:
public static int numberofTrailingZeroes(int i)>
パラメーター:
i : int value whose trailing zeroes to count in twos complement form>
20.highestOneBit() : 指定された値の最上位の 1 ビットの位置に、最大で 1 つの 1 ビットを含む値を返します。指定された値が 0 の場合、つまり数値が 0000 0000 0000 1111 の場合、この関数は 0000 0000 0000 1000 (指定された数値の最大 1 ビット) を返します。
構文:
public static int highestOneBit(int i)>
パラメーター:
i : int value>
21. 最低ワンビット() : 指定された値の最下位 1 ビットの位置に最大 1 ビットの値を返します。指定された値が 0 の場合、つまり数値が 0000 0000 0000 1111 の場合、この関数は 0000 0000 0000 0001 (指定された数値の最大 1 ビット) を返します。
構文:
public static int LowestOneBit(int i)>
パラメーター:
i : int value>
22. 等しい() : 2 つの Integer オブジェクトの同等性を比較するために使用されます。両方のオブジェクトに同じ int 値が含まれている場合、このメソッドは true を返します。等しいかどうかをチェックする場合にのみ使用してください。それ以外の場合はすべて、compareTo メソッドを優先する必要があります。
構文:
public boolean equals(Object obj)>
パラメーター:
obj : object to compare with>
23.compareTo() : 2 つの Integer オブジェクトを数値的に等しいかどうか比較するために使用されます。これは、数値が等しいかどうかについて 2 つの整数値を比較するときに使用する必要があります。これは、小さい値と大きい値を区別するためです。 0,0 より小さい値、より小さい、等しい、より大きい場合は 0 より大きい値を返します。
構文:
public int compareTo(Integer b)>
パラメーター:
b : Integer object to compare with>
24. 比較() : 2 つのプリミティブ int 値を数値的に等しいかどうか比較するために使用されます。静的メソッドなので、Integer のオブジェクトを作成せずに使用できます。
構文:
public static int compare(int x,int y)>
パラメーター:
無料と無料
x : int value y : another int value>
25. サイン() : 負の値の場合は -1、0 の場合は 0、0 より大きい値の場合は +1 を返します。
構文:
public static int signum(int val)>
パラメーター:
val : int value for which signum is required.>
26. リバース() : 指定された int 値の 2 の補数形式でビットの順序を反転したプリミティブ int 値を返します。
構文:
public static int reverseBytes(int val)>
パラメーター:
val : int value whose bits to reverse in order.>
27. reverseBytes() : 指定された int 値の 2 の補数形式でバイトの順序を反転したプリミティブ int 値を返します。
構文:
public static int reverseBytes(int val)>
パラメーター:
val : int value whose bits to reverse in order.>
28. static int CompareUnsigned(int x, int y) : このメソッドは、値を符号なしとして扱い、2 つの int 値を数値的に比較します。
構文:
public static int compareUnsigned(int x, int y)>
29. static int DivisionUnsigned(int 被除数, int 除数) : このメソッドは、最初の引数を 2 番目の引数で割った符号なしの商を返します。ここで、各引数と結果は符号なしの値として解釈されます。
構文:
public static int divideUnsigned(int dividend, int divisor)>
30. static int max(int a, int b) : このメソッドは、Math.max を呼び出したかのように、2 つの int 値の大きい方を返します。
構文:
public static int max(int a, int b)>
31. 静的 int min(int a, int b) : このメソッドは、Math.min を呼び出したかのように、2 つの int 値のうち小さい方を返します。
構文:
public static int min(int a, int b)>
32. static int parseUnsignedInt(CharSequence s, int beginIndex, int endIndex, int radix) : このメソッドは、CharSequence 引数を、指定された基数の unsigned int として解析します。指定された beginIndex から始まり、endIndex – 1 まで続きます。
構文:
public static int parseUnsignedInt(CharSequence s, int beginIndex, int endIndex, int radix) throws NumberFormatException>
33. 静的 int parseUnsignedInt(String s) : このメソッドは、文字列引数を符号なし 10 進整数として解析します。
構文:
public static int parseUnsignedInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException>
34. static int parseUnsignedInt(String s, int radix) : このメソッドは、文字列引数を 2 番目の引数で指定された基数の符号なし整数として解析します。
構文:
public static int parseUnsignedInt(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatException>
35. 静的 int 剰余Unsigned(int 被除数, int 除数) : このメソッドは、最初の引数を 2 番目の引数で除算した符号なしの剰余を返します。ここで、各引数と結果は符号なしの値として解釈されます。
構文:
public static int remainderUnsigned(int dividend, int divisor)>
36. 静的 int sum(int a, int b) : このメソッドは、+ 演算子に従って 2 つの整数を加算します。
構文:
public static int sum(int a, int b)>
37. 静的long toUnsignedLong(int x) : このメソッドは、引数を符号なし変換によってlongに変換します。
構文:
public static long toUnsignedLong(int x)>
38. 静的文字列 toUnsignedString(int i) : このメソッドは、引数の文字列表現を符号なし 10 進数値として返します。
構文:
public static String toUnsignedString(int i, int radix)>
ジャワ
// Java program to illustrate> // various Integer class methods> public> class> Integer_test {> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >int> b =>55>;> >String bb =>'45'>;> >// Construct two Integer objects> >Integer x =>new> Integer(b);> >Integer y =>new> Integer(bb);> >// xxxValue can be used to retrieve> >// xxx type value from int value.> >// xxx can be int,byte,short,long,double,float> >System.out.println(>'bytevalue(x) = '> >+ x.byteValue());> >System.out.println(>'shortvalue(x) = '> >+ x.shortValue());> >System.out.println(>'intvalue(x) = '> + x.intValue());> >System.out.println(>'longvalue(x) = '> >+ x.longValue());> >System.out.println(>'doublevalue(x) = '> >+ x.doubleValue());> >System.out.println(>'floatvalue(x) = '> >+ x.floatValue());> >int> value =>45>;> >// bitcount() : can be used to count set bits> >// in twos complement form of the number> >System.out.println(>'Integer.bitcount(value)='> >+ Integer.bitCount(value));> >// numberOfTrailingZeroes and numberOfLeadingZeroes> >// can be used to count prefix and postfix sequence> >// of 0> >System.out.println(> >'Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(value)='> >+ Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(value));> >System.out.println(> >'Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(value)='> >+ Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(value));> >// highestOneBit returns a value with one on highest> >// set bit position> >System.out.println(>'Integer.highestOneBit(value)='> >+ Integer.highestOneBit(value));> >// highestOneBit returns a value with one on lowest> >// set bit position> >System.out.println(>'Integer.lowestOneBit(value)='> >+ Integer.lowestOneBit(value));> >// reverse() can be used to reverse order of bits> >// reverseBytes() can be used to reverse order of> >// bytes> >System.out.println(>'Integer.reverse(value)='> >+ Integer.reverse(value));> >System.out.println(>'Integer.reverseBytes(value)='> >+ Integer.reverseBytes(value));> >// signum() returns -1,0,1 for negative,0 and> >// positive values> >System.out.println(>'Integer.signum(value)='> >+ Integer.signum(value));> >// hashcode() returns hashcode of the object> >int> hash = x.hashCode();> >System.out.println(>'hashcode(x) = '> + hash);> >// equals returns boolean value representing> >// equality> >boolean> eq = x.equals(y);> >System.out.println(>'x.equals(y) = '> + eq);> >// compare() used for comparing two int values> >int> e = Integer.compare(x, y);> >System.out.println(>'compare(x,y) = '> + e);> >// compareTo() used for comparing this value with> >// some other value> >int> f = x.compareTo(y);> >System.out.println(>'x.compareTo(y) = '> + f);> >}> }> |
>
>
出力:
bytevalue(x) = 55 shortvalue(x) = 55 intvalue(x) = 55 longvalue(x) = 55 doublevalue(x) = 55.0 floatvalue(x) = 55.0 Integer.bitcount(value)=4 Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(value)=0 Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(value)=26 Integer.highestOneBit(value)=32 Integer.lowestOneBit(value)=1 Integer.reverse(value)=-1275068416 Integer.reverseBytes(value)=754974720 Integer.signum(value)=1 hashcode(x) = 55 x.equals(y) = false compare(x,y) = 1 x.compareTo(y) = 1>
Java での整数ラッパー クラスの初期化:
タイプ 1: 直接初期化:
ヒープメモリ上の定数空間内にIntegerクラスの定数オブジェクトが作成されます。定数のスペース: ヒープ メモリに定数用のスペースがあることをよりよく理解するために想像してください。
例:
Integer x = 200; //initializing directly x = 300; //modifying x x = 10; //modifying x again>
整数 x = 200
- コンパイラは上記のステートメントを次のように変換します。 整数 x=Integer.valueOf(200) 。 これはとして知られています オートボクシング 。プリミティブ整数値 200 がオブジェクトに変換されます。
(オートボックス化とボックス化解除について理解するには、ここを確認してください: )
- x は定数の空間に存在する 200 を指します。図1を参照してください。
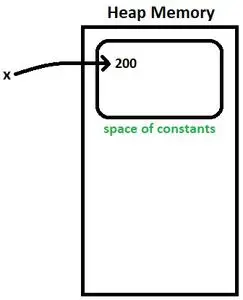
図1
x = 300
Java配列リストのソート
- x は直接初期化される Integer クラス オブジェクトであるため、オートボックス化が再度実行されます。
- 注記: 直接初期化されたオブジェクト(x)は定数であるため変更できません。新しい定数 (300) をポイントしてオブジェクトを変更しようとすると、古い定数 (200) はヒープ メモリ内に存在しますが、オブジェクトは新しい定数をポイントすることになります。
- x は定数の空間に存在する 300 を指します。図2を参照してください。
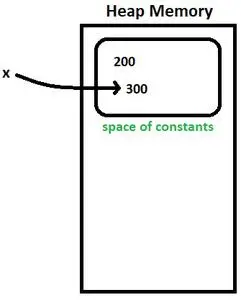
図2
x = 10
- 注記: 値 -128 ~ 127 のデフォルトでは、Integer.valueOf() メソッドは Integer の新しいインスタンスを作成しません。キャッシュから値を返します。
- x ポイント 10 はキャッシュに存在します。
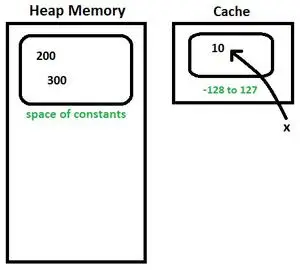
図3
次回 x = 200 または x=300 を代入すると、定数の空間にすでに存在する値 200 または 300 を指すことになります。これら 2 つの値以外の値を x に代入すると、新しい定数が作成されます。
(よりよく理解するには、整数ラッパー クラスの比較トピックを確認してください)
タイプ 2: 動的に初期化する:
定数ではない Integer クラス オブジェクトは定数の空間の外に作成されます。また、定数の空間内に整数定数も作成します。変数は、Integer 定数ではなく、Integer オブジェクトを指します。
例:
Integer a = new Integer(250); //Initializing dynamically a = 350; //Type 1 initialization>
整数 a = 新しい整数(250)
- 250は定数の空間の内と外に生み出されます。変数「a」は、定数の空間の外側にある値を指します。図4を参照してください。
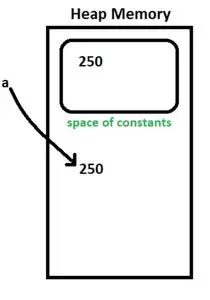
図4
a = 350;
- オートボクシング後、「a」は 350 を指します。図 5 を参照してください。
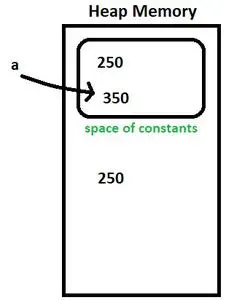
図5
次回 a = 250 を割り当てると、同じ値ですでに存在するオブジェクトを指すのではなく、新しいオブジェクトが作成されます。
参考文献: 公式 Java ドキュメント
