ミニマックスは一種のバックトラッキング アルゴリズムで、対戦相手も最適なプレーをしていると仮定して、プレーヤーにとって最適な手を見つけるために意思決定やゲーム理論で使用されます。三目並べ、バックギャモン、マンカラ、チェスなどの 2 人用ターンベース ゲームで広く使用されています。
ミニマックスでは、2 人のプレーヤーはマキシマイザーとミニマイザーと呼ばれます。の マキシマイザー 可能な限り最高のスコアを取得しようとしますが、 ミニマイザー 逆のことをして、可能な限り低いスコアを取得しようとします。
すべてのボードの状態には、それに関連付けられた値があります。特定の状態でマキシマイザーが優勢であれば、ボードのスコアは何らかのプラスの値になる傾向があります。そのボードの状態でミニマイザーが優位にある場合、マイナスの値になる傾向があります。ボードの値は、ゲームの種類ごとに固有のヒューリスティックによって計算されます。
例:
以下に示すように、4 つの最終状態があり、最終状態に到達するパスが完全な二分木のルートから 4 つの葉であるゲームを考えてみましょう。あなたが最大化プレイヤーであり、移動する最初のチャンスがあると仮定します。つまり、あなたはルートにいて、対戦相手は次のレベルにいます。 対戦相手も最適なプレーをすることを考慮すると、最大化プレイヤーとしてどの動きをしますか?
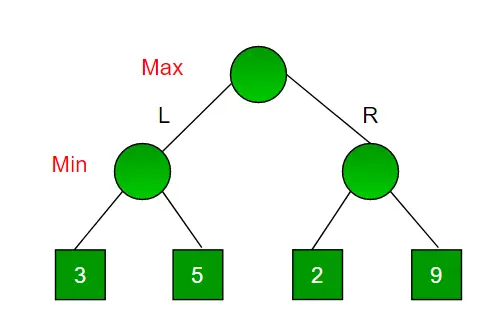
これはバックトラックベースのアルゴリズムであるため、可能なすべての手を試してからバックトラックして決定を下します。
- マキシマイザーが左へ:今度はミニマイザーの番です。ミニマイザーには 3 と 5 の間で選択肢ができるようになりました。ミニマイザーであるため、両方の中で最も小さいもの、つまり 3 が確実に選択されます。
- マキシマイザーが右に進む: ここで、ミニマイザーの番になります。ミニマイザーには 2 ~ 9 の選択肢があります。2 つの値の中で最小である 2 を選択します。
マキシマイザーであるため、より大きな値である 3 を選択します。したがって、マキシマイザーの最適な動きは左に移動することであり、最適な値は 3 です。
ゲームツリーは以下のようになります。

上のツリーは、マキシマイザーが左右に移動したときに考えられる 2 つのスコアを示しています。
注: 右側のサブツリーに値 9 があっても、ミニマイザーはそれを選択しません。私たちは常に、相手が最適なプレーをしていると想定しなければなりません。
以下は同じ実装です。
C++
アナコンダ vs パイソンヘビ
// A simple C++ program to find> // maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is> // of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>bool> isMax,> >int> scores[],>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e> >// leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer,> >// find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> int> log2(>int> n)> {> >return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> scores[] = {3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23};> >int> n =>sizeof>(scores)/>sizeof>(scores[0]);> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >cout <<>'The optimal value is : '> << res << endl;> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
ジャワ
// A simple java program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> import> java.io.*;> class> GFG {> > // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> >static> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>boolean> isMax,> >int> scores[],>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.max(minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2>,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2> +>1>,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.min(minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2>,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2> +>1>,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> >static> int> log2(>int> n)> {> return> (n==>1>)?>0> :>1> + log2(n/>2>);> }> // Driver code> >public> static> void> main (String[] args) {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> scores[] = {>3>,>5>,>2>,>9>,>12>,>5>,>23>,>23>};> >int> n = scores.length;> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(>0>,>0>,>true>, scores, h);> >System.out.println(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > >}> }> // This code is contributed by vt_m> |
>
>
C#
// A simple C# program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> using> System;> public> class> GFG> {> > // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> static> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>bool> isMax,> >int> []scores,>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.Max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.Min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> static> int> log2(>int> n)> {> >return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> // Driver code> static> public> void> Main ()> {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> []scores = {3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23};> >int> n = scores.Length;> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >Console.WriteLine(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > }> }> // This code is contributed by ajit.> |
>
>
Python3
Javaの揮発性キーワード
# A simple Python3 program to find> # maximum score that> # maximizing player can get> import> math> def> minimax (curDepth, nodeIndex,> >maxTurn, scores,> >targetDepth):> ># base case : targetDepth reached> >if> (curDepth>=>=> targetDepth):> >return> scores[nodeIndex]> > >if> (maxTurn):> >return> max>(minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2>,> >False>, scores, targetDepth),> >minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2> +> 1>,> >False>, scores, targetDepth))> > >else>:> >return> min>(minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2>,> >True>, scores, targetDepth),> >minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2> +> 1>,> >True>, scores, targetDepth))> > # Driver code> scores>=> [>3>,>5>,>2>,>9>,>12>,>5>,>23>,>23>]> treeDepth>=> math.log(>len>(scores),>2>)> print>(>'The optimal value is : '>, end>=> '')> print>(minimax(>0>,>0>,>True>, scores, treeDepth))> # This code is contributed> # by rootshadow> |
>
>
JavaScript
パンダの軸
> // Javascript program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> >function> minimax(depth, nodeIndex, isMax,> >scores, h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> > >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> > >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> > // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> >function> log2(n)> {> return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> > // Driver Code> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >let scores = [3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23];> >let n = scores.length;> >let h = log2(n);> >let res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >document.write(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > > > |
>
>
出力:
The optimal value is: 12>
時間計算量 : O(b^d) b は分岐係数、d はグラフまたはツリーの深さまたは層の数です。
空間の複雑さ : O(bd) ここで、b は d への分岐係数であり、DFS と同様のツリーの最大深さです。
この記事の目的は、簡単な例で Minimax を紹介することです。
- 上の例では、プレイヤーの選択肢は 2 つだけです。一般に、より多くの選択肢がある可能性があります。その場合、考えられるすべての動きを繰り返して最大/最小を見つける必要があります。たとえば、三目並べでは、最初のプレーヤーは 9 つの可能な手を実行できます。
- 上の例では、スコア (ゲーム ツリーの葉) が与えられます。典型的なゲームの場合、これらの値を導き出す必要があります。
Minimax アルゴリズムを使用した三目並べについては、間もなく取り上げる予定です。
この記事は次の寄稿者です アクシャイ・L・アラディヤ。
