std::shared_ptr C++11 で導入されたスマート ポインターの 1 つです。単純なポインターとは異なり、管理オブジェクトの参照カウントを追跡する制御ブロックが関連付けられています。この参照カウントは、同じオブジェクトを指すshared_ptrインスタンスのすべてのコピー間で共有され、適切なメモリ管理と削除が保証されます。
前提条件: C++ のポインター 、 C++ のスマート ポインター 。
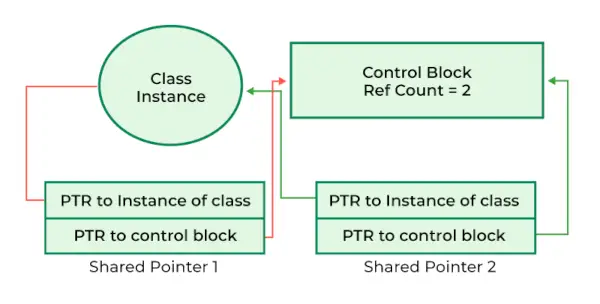
C++ のシェアード ポインター
std::shared_ptr の構文
T 型のshared_ptrは次のように宣言できます。
std::shared_ptr ptr_name;>
shared_ptr オブジェクトの初期化
次のメソッドを使用して、shared_ptr を初期化できます。
1. 新しいポインタを使用した初期化
shared_ptr ptr (new T()); shared_ptr ptr = make_shared (new T());>
2. 既存のポインタを使用した初期化
shared_ptr ptr(already_existing_pointer); shared_ptr ptr = make_shared(already_existing_pointer);>
shared_ptrのメンバーメソッド
以下は、shared_ptr に関連付けられたいくつかのメンバーです。
| 方法 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| リセット() | std::shared_ptr を空にリセットし、管理オブジェクトの所有権を解放します。 |
| use_count() | 所有権を共有する std::shared_ptr インスタンスの数を示す、現在の参照カウントを返します。 |
| 個性的() | オブジェクトを所有する std::shared_ptr が 1 つだけであるかどうかを確認します (参照カウントは 1)。 |
| 得る() | 管理対象オブジェクトへの生のポインタを返します。この方法を使用する場合は注意してください。 |
| スワップ(shr_ptr2) | 2 つの std::shared_ptr インスタンスの内容 (所有権) を交換します。 |
std::shared_ptr の例
例 1:
C++
>
>出力
0x1365c20 A::show() A::show() 0x1365c20 0x1365c20 2 2 0 1 0x1365c20>
例 2:
C++
// C++ program to illustrate the use of make_shared> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> int> main()> {> >// Creating shared pointers using std::make_shared> >shared_ptr<>int>>shr_ptr1 = make_shared<>int>>(42);>> int>>shr_ptr2 = make_shared<>int>>(24);>> >// (*)> >cout << 'Value 1: ' << *shr_ptr1 << endl;> >cout << 'Value 2: ' << *shr_ptr2 << endl;> >// Using the assignment operator (=) to share ownership> >shared_ptr<>int>>shr_ptr3 = shr_ptr1;>> >// Checking if shared pointer 1 and shared pointer 3> >// point to the same object> >if> (shr_ptr1 == shr_ptr3) {> >cout << 'shared pointer 1 and shared pointer 3 '> >'point to the same object.'> ><< endl;> >}> >// Swapping the contents of shared pointer 2 and shared> >// pointer 3> >shr_ptr2.swap(shr_ptr3);> >// Checking the values after the swap> >cout << 'Value 2 (after swap): ' << *shr_ptr2 << endl;> >cout << 'Value 3 (after swap): ' << *shr_ptr3 << endl;> >// Using logical operators to check if shared pointers> >// are valid> >if> (shr_ptr1 && shr_ptr2) {> >cout << 'Both shared pointer 1 and shared pointer '> >'2 are valid.'> ><< endl;> >}> >// Resetting a shared pointer> >shr_ptr1.reset();> }> |
>
>出力
Value 1: 42 Value 2: 24 shared pointer 1 and shared pointer 3 point to the same object. Value 2 (after swap): 42 Value 3 (after swap): 24 Both shared pointer 1 and shared pointer 2 are valid.>
例 3: std::shared_ptr を使用したリンク リストの実装
C++
#include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Define a singly linked list node> struct> Node {> >int> data;> >shared_ptr next;> >Node(>int> val)> >: data(val)> >, next(NULL)> >{> >}> };> class> LinkedList {> public>:> >LinkedList()> >: head(NULL)> >{> >}> >// Insert a new node at the end of the linked list> >void> insert(>int> val)> >{> >shared_ptr newNode = make_shared(val);> >if> (!head) {> >head = newNode;> >}> >else> {> >shared_ptr current = head;> >while> (current->次へ) {>> >current = current->次へ;>> >current->next = newNode;>> >}> >}> >// Delete a node with a given value from the linked list> >void> del(>int> val)> >{> >if> (!head) {> >return>;> >}> >if> (head->データ == val) {> >head = head->次へ;>> ;> >}> >shared_ptr current = head;> >while> (current->次へ> >&& current->次->データ != val) {> >current = current->次へ;>> >if> (current->次 && 現在->次->データ == val) {> >current->次 = 現在->次->次;>> >}> >}> >// Traverse and print the linked list> >void> Print()> >{> >shared_ptr current = head;> >while> (current) {> >cout current = current->次; }<< 'NULL' << endl; } private: shared_ptr head; }; int main() { LinkedList linkedList; // Insert nodes into the linked list linkedList.insert(1); linkedList.insert(2); linkedList.insert(3); // Print the linked list cout << 'Linked List: '; linkedList.Print(); // Delete a node and print the updated linked list linkedList.del(2); cout << 'Linked List after deleting 2: '; linkedList.Print(); return 0; }> |
>
Javaの文字列結合
>出力
Linked List: 1 ->2 -> 3 -> NULL 2 を削除した後のリンク リスト: 1 -> 3 -> NULL>>
