インメモリデータベースとは何ですか
インメモリ データベースは、データの保存にディスク領域ではなくシステム メモリに依存します。メモリアクセスはディスクアクセスよりも速いためです。データを永続化する必要がない場合は、インメモリ データベースを使用します。インメモリ データベースは組み込みデータベースです。デフォルトでは、インメモリ データベースは揮発性であり、アプリケーションを再起動すると、保存されているデータはすべて失われます。
広く使用されているインメモリ データベースは次のとおりです。 H2、HSQLDB (ハイパーSQLデータベース) 、 そして アパッチダービー。 構成を自動的に作成します。
永続性とインメモリ データベース
永続データベースは、データを物理メモリに永続化します。データベース サーバーがバウンスした場合でも、データは利用できます。一般的な永続データベースには、次のようなものがあります。 オラクル、 MySQL 、ポストグル、 等
Pythonの差分
の場合、 インメモリデータベース、 データストア システムメモリ 。プログラムを閉じるとデータが失われます。役に立ちます 少し ■ (概念実証)、本番アプリケーション向けではありません。広く使用されているインメモリ データベースは次のとおりです。 H2.
H2データベースとは
H2 です 組み込み、オープンソース、 そして メモリ内 データベース。で書かれたリレーショナル データベース管理システムです。 ジャワ 。それは クライアントサーバー 応用。一般的に使用されるのは、 単体テスト 。データをディスク上に保持するのではなく、メモリにデータを保存します。
利点
- ゼロ構成
- 使い方は簡単です。
- 軽くて速いです。
- 実データベースとメモリ内データベースを切り替えるための簡単な構成を提供します。
- 標準 SQL および JDBC API をサポートします。
- データベース内で管理するための Web コンソールを提供します。
H2 データベースの構成
アプリケーションで H2 データベースを使用したい場合は、pom.xml ファイルに次の依存関係を追加する必要があります。
com.h2database h2 runtime
依存関係を追加した後、設定する必要があります データ ソース URL、ドライバー クラス名、ユーザー名、 そして パスワード H2データベースの。 Spring Boot は、これらのプロパティを構成する簡単な方法を提供します。 アプリケーションのプロパティ ファイル。
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver spring.datasource.username=sa spring.datasource.password= spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
の中に spring.datasource.url 財産、 私 インメモリデータベースの名前であり、 テストデータベース は、H2 がデフォルトで提供するスキーマの名前です。独自のスキーマとデータベースを定義することもできます。デフォルトのユーザー名は次のとおりです の上 空のパスワードは 空の パスワード。ユーザー名とパスワードを変更したい場合は、これらの値をオーバーライドできます。
データを H2 データベースに保存する
H2 データベースにデータを永続化したい場合は、データをファイルに保存する必要があります。同じことを実現するには、データソース URL プロパティを変更する必要があります。
#persist the data spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:file:/data/sampledata spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:C:/data/sampledata
上記のプロパティでは、 サンプルデータ はファイル名です。
スキーマの作成とデータの入力
を作成することでスキーマを定義できます。 SQL 内のファイル リソース フォルダー (src/main/resource)。
スキーマ.sql
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS CITY; CREATE TABLE CITY ( City_code INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, city_name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, city_pincode INT(8) NOT NULL );
を作成することでテーブルにデータを入力できます。 SQL 内のファイル リソース フォルダー (src/main/resource)。
データ.SQL
INSERT INTO CITY VALUES (11, 'Delhi', 110001); INSERT INTO CITY VALUES (12, 'Kanpur', 208001); INSERT INTO CITY VALUES (13, 'Lucknow', 226001);
Spring Boot は自動的に データ.SQL ファイルを作成し、アプリケーションの起動時に H2 データベースに対して実行します。
H2 コンソール
デフォルトでは、H2 データベースのコンソール ビューは無効になっています。 H2 データベースにアクセスする前に、次のプロパティを使用してデータベースを有効にする必要があります。
Javaの擬似コード
#enabling the H2 console spring.h2.console.enabled=true
H2 コンソールを有効にすると、URL http://localhost:8080/h2-console を呼び出してブラウザで H2 コンソールにアクセスできるようになります。次の図は、H2 データベースのコンソール ビューを示しています。
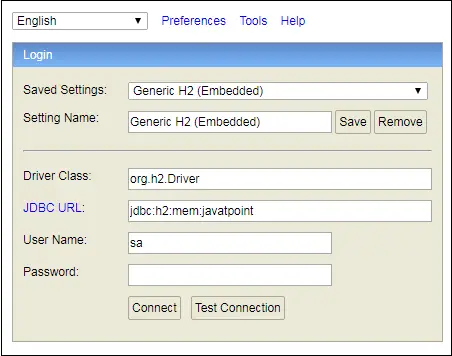
上のスクリーンショットでは、という名前の独自のデータベースを定義しています。 ジャバトポイント 。
Spring Boot H2 の例
H2 データベースを使用して Spring Boot アプリケーションをセットアップしてみましょう。
ステップ1: Spring Initializr http://start.spring.io を開きます。
ステップ2: Spring Boot バージョンを選択します 2.3.0.M1。
ステップ2: を提供します。 グループ 名前。私たちが提供したのは、 com.javatpoint。
ステップ 3: を提供します。 アーティファクト 同上。私たちが提供したのは、 スプリングブート H2 データベースの例。
ステップ5: 依存関係を追加する Spring Web、Spring Data JPA、 そして H2 データベース。
ステップ6: クリックしてください 生成する ボタン。 「生成」ボタンをクリックすると、プロジェクトがラップされます。 瓶 ファイルを作成し、ローカル システムにダウンロードします。

ステップ 7: 抽出する Jar ファイルを選択し、STS ワークスペースに貼り付けます。
ステップ8: 輸入 プロジェクトフォルダーをSTSにコピーします。
ファイル -> インポート -> 既存の Maven プロジェクト -> 参照 -> フォルダー spring-boot-h2-database-example を選択 -> 完了
キャットティンプ
インポートには時間がかかります。
ステップ9: という名前のパッケージを作成します。 com.javatpoint.model フォルダ内に src/メイン/java。
ステップ 10: パッケージ内にモデルクラスを作成する com.javatpoint.model。 という名前のモデルクラスを作成しました。 学生。 Books クラスでは、次のことを行いました。
- 4 つの変数を定義する ID、年齢、名前、 そして
- ゲッターとセッターを生成します。
ファイルを右クリック→「ソース」→「ゲッターとセッターの生成」を選択します。 - クラスを次のようにマークします 実在物 注釈を使用して @実在物。
- クラスを次のようにマークします テーブル 注釈を使用して名前を付ける @テーブル。
- 各変数を次のように定義します カラム 注釈を使用して @カラム。
Student.java
package com.javatpoint.model; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Table; //mark class as an Entity @Entity //defining class name as Table name @Table public class Student { //mark id as primary key @Id //defining id as column name @Column private int id; //defining name as column name @Column private String name; //defining age as column name @Column private int age; //defining email as column name @Column private String email; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getEmail() { return email; } public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; } } ステップ 11: という名前のパッケージを作成します。 com.javatpoint.controller フォルダ内に src/メイン/java。
ステップ 12: パッケージ内にコントローラークラスを作成する com.javatpoint.controller 。という名前のコントローラークラスを作成しました。 StudentController 。 StudentController クラスでは、次のことを行いました。
- クラスを次のようにマークします レストコントローラー 注釈を使用して @RestController。
- 自動配線 学生サービス アノテーションを使用したクラス @Autowired 。
- 次のメソッドを定義します。
getAllStudent(): すべての生徒のリストを返します。
StudentController.java
package com.javatpoint.controller; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import com.javatpoint.model.Student; import com.javatpoint.service.StudentService; //creating RestController @RestController public class StudentController { //autowired the StudentService class @Autowired StudentService studentService; //creating a get mapping that retrieves all the students detail from the database @GetMapping('/student') private List getAllStudent() { return studentService.getAllStudent(); } //creating a get mapping that retrieves the detail of a specific student @GetMapping('/student/{id}') private Student getStudent(@PathVariable('id') int id) { return studentService.getStudentById(id); } //creating a delete mapping that deletes a specific student @DeleteMapping('/student/{id}') private void deleteStudent(@PathVariable('id') int id) { studentService.delete(id); } //creating post mapping that post the student detail in the database @PostMapping('/student') private int saveStudent(@RequestBody Student student) { studentService.saveOrUpdate(student); return student.getId(); } } ステップ 13: という名前のパッケージを作成します。 com.javatpoint.service フォルダ内に src/メイン/java。
ステップ 14: を作成します サービス クラス。という名前のサービスクラスを作成しました。 学生サービス パッケージの中に com.javatpoint.service。
StudentService.java
package com.javatpoint.service; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import com.javatpoint.model.Student; import com.javatpoint.repository.StudentRepository; @Service public class StudentService { @Autowired StudentRepository studentRepository; //getting all student records public List getAllStudent() { List students = new ArrayList(); studentRepository.findAll().forEach(student -> students.add(student)); return students; } //getting a specific record public Student getStudentById(int id) { return studentRepository.findById(id).get(); } public void saveOrUpdate(Student student) { studentRepository.save(student); } //deleting a specific record public void delete(int id) { studentRepository.deleteById(id); } } ステップ 15: という名前のパッケージを作成します。 com.javatpoint.リポジトリ フォルダ内に src/メイン/java。
ステップ 16: を作成します リポジトリ インターフェース。という名前のリポジトリ インターフェイスを作成しました。 StudentRepository パッケージの中に com.javatpoint.リポジトリ。 それは、 Crudリポジトリ インターフェース。
StudentRepository.java
package com.javatpoint.repository; import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository; import com.javatpoint.model.Student; public interface StudentRepository extends CrudRepository { } 次に、データソースを構成します URL、ドライバークラス名、ユーザー名、 そして パスワード、 の中に アプリケーションのプロパティ ファイル。
ステップ 17: を開きます アプリケーションのプロパティ ファイルを作成し、次のプロパティを構成します。
アプリケーションのプロパティ
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:javatpoint spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver spring.datasource.username=sa spring.datasource.password= spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect #enabling the H2 console spring.h2.console.enabled=true
注: H2 コンソールを有効にすることを忘れないでください。
すべてのクラスとパッケージを作成すると、プロジェクト ディレクトリは次のようになります。

次に、アプリケーションを実行します。
Javaの部分文字列の例
ステップ 18: 開ける SpringBootH2DatabaseExampleApplication.java ファイルを作成し、Java アプリケーションとして実行します。
SpringBootH2DatabaseExampleApplication.java
package com.javatpoint; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringBootH2DatabaseExampleApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootH2DatabaseExampleApplication.class, args); } } 次のステップでは、残りのクライアントを使用します 郵便屋さん を送信するための 役職 そして 得る リクエスト 。 Postman がシステムにインストールされていない場合は、次の手順に従います。
- ポストマンをダウンロードする https://www.getpostman.com/downloads/ またはブラウザにGoogle Chrome拡張機能を追加します https://bit.ly/1HCOCwF 。
- ポストマンを起動して、 サインアップ 。ユーザー名を作成します。という名前のユーザーを作成しました ジャバトポイント そしてクリックしました 提出する
ステップ 19: を開きます 郵便屋さん そして次のことを実行します。
- を選択 役職
- URL http://localhost:8080/student を呼び出します。
- を選択 体
- コンテンツタイプを選択してください JSON (アプリケーション/json)。
- データを挿入します。本文に次のデータを挿入しました。
{ 'id': '001', 'age': '23', 'name': 'Amit', 'email': '[email protected]' } - クリックしてください 送信
リクエストが正常に実行されると、 ステータス:200 OK 。これは、レコードがデータベースに正常に挿入されたことを意味します。
同様に、次のデータを挿入しました。
{ 'id': '002', 'age': '24', 'name': 'Vadik', 'email': '[email protected]' } { 'id': '003', 'age': '21', 'name': 'Prateek', 'email': '[email protected]' } { 'id': '004', 'age': '25', 'name': 'Harsh', 'email': '[email protected]' } { 'id': '005', 'age': '24', 'name': 'Swarit', 'email': '[email protected]' } H2 コンソールにアクセスしてデータを確認してみましょう。
ステップ 20: ブラウザを開いて、URL http://localhost:8080/h2-console を呼び出します。クリックしてください 接続する 以下に示すように、ボタンをクリックします。

をクリックした後、 接続する ボタンをクリックすると、 学生 以下に示すように、データベース内のテーブル。

ステップ21: クリックしてください 学生 テーブルをクリックし、 走る ボタン。この表は、本文に挿入したデータを示しています。

ステップ22: 郵便配達員を開いて、 得る リクエスト。データベースに挿入したデータを返します。

を送信しましょう 得る URL http://localhost:8080/student/{id} でリクエストします。 URL http://localhost:8080/student/3 を呼び出しました。 ID が 3 の学生の詳細を返します。
配列と配列リストの違い

同様に、 消去 リクエスト。 ID が 2 の学生レコードを削除するとします。
生徒の記録を削除するには、 消去 URL http://localhost:8080/student/2 でリクエストします。 ID が次の学生であることがわかります。 2 データベースから削除されました。

H2 データベースのサンプル プロジェクトをダウンロード
