この記事では、Java プログラミング言語を使用してファイルに書き込むさまざまな方法を見ていきます。 Java の Java FileWriter クラスは、Java でのファイル処理で使用されるため、文字指向のデータをファイルに書き込むために使用されます。このクラスは文字指向のクラスです。
沢山あります Java でファイルに書き込む方法 次のように、目的を達成できるクラスやメソッドが多数あるためです。
- 使用する writeString() 方法
- FileWriter クラスの使用
- BufferedWriter クラスの使用
- FileOutputStream クラスの使用
方法 1: writeString() メソッドを使用する
このメソッドは Java バージョン 11 でサポートされています。このメソッドは 4 つのパラメータを取ることができます。これらは、ファイル パス、文字シーケンス、文字セット、およびオプションです。最初の 2 つのパラメータは、このメソッドがファイルに書き込むために必須です。文字をファイルの内容として書き込みます。ファイル パスを返し、4 種類の例外をスローできます。ファイルの内容が短い場合に使用するとよいでしょう。
例: の使用法を示しています。 writeString() ファイルにデータを書き込むための Files クラスの下にあるメソッド。別のクラス Path は、コンテンツが書き込まれるパスをファイル名に割り当てるために使用されます。 File クラスには別の名前のメソッドがあります readString() コードで使用されている既存のファイルの内容を読み取り、内容がファイルに正しく書き込まれているかどうかを確認します。
ジャワ
aws赤方偏移
// Java Program to Write Into a File> // using writeString() Method> // Importing required classes> import> java.io.IOException;> import> java.nio.file.Files;> import> java.nio.file.Path;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >throws> IOException> >{> >// Assigning the content of the file> >String text> >=>'Welcome to geekforgeeks
Happy Learning!'>;> >// Defining the file name of the file> >Path fileName = Path.of(> >'/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'>);> >// Writing into the file> >Files.writeString(fileName, text);> >// Reading the content of the file> >String file_content = Files.readString(fileName);> >// Printing the content inside the file> >System.out.println(file_content);> >}> }> |
>
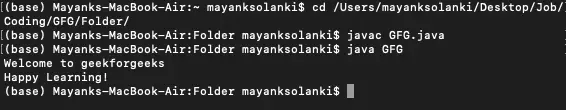
>出力
Welcome to geekforgeeks Happy Learning!>
方法 2: FileWriter クラスを使用する
ファイルの内容が短い場合は、FileWriter クラスを使用してファイルに書き込むことも良い方法です。また、writeString() メソッドと同様に、文字のストリームをファイルのコンテンツとして書き込みます。このクラスのコンストラクターは、デフォルトの文字エンコーディングとデフォルトのバッファ サイズをバイト単位で定義します。
次の例は、FileWriter クラスを使用してコンテンツをファイルに書き込む方法を示しています。ファイルに書き込むファイル名を使用して FileWriter クラスのオブジェクトを作成する必要があります。次に、write() メソッドを使用して、テキスト変数の値をファイルに書き込みます。ファイルの書き込み時にエラーが発生した場合は、IOException がスローされ、catch ブロックからエラー メッセージが出力されます。
JavaでCSVファイルから読み取る方法
例:
ジャワ
// Java Program to Write into a File> // using FileWriterClass> // Importing required classes> import> java.io.FileWriter;> import> java.io.IOException;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Content to be assigned to a file> >// Custom input just for illustration purposes> >String text> >=>'Computer Science Portal techcodeview.com'>;> >// Try block to check if exception occurs> >try> {> >// Create a FileWriter object> >// to write in the file> >FileWriter fWriter =>new> FileWriter(> >'/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'>);> >// Writing into file> >// Note: The content taken above inside the> >// string> >fWriter.write(text);> >// Printing the contents of a file> >System.out.println(text);> >// Closing the file writing connection> >fWriter.close();> >// Display message for successful execution of> >// program on the console> >System.out.println(> >'File is created successfully with the content.'>);> >}> >// Catch block to handle if exception occurs> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Print the exception> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >}> }> |
>
文字列をJavaに変換する
>出力
File is created successfully with the content.>

方法 3: BufferedWriter クラスを使用する
これは、文字出力ストリームにテキストを書き込むために使用されます。デフォルトのバッファ サイズがありますが、大きなバッファ サイズを割り当てることができます。文字、文字列、配列を記述する場合に便利です。プロンプト出力が必要ない場合は、ファイルにデータを書き込むためのライター クラスでこのクラスをラップすることをお勧めします。
例:
ジャワ
// Java Program to write into a File> // Using BufferedWriter Class> // Importing java input output libraries> import> java.io.BufferedWriter;> import> java.io.FileWriter;> import> java.io.IOException;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Assigning the file content> >// Note: Custom contents taken as input to> >// illustrate> >String text> >=>'Computer Science Portal techcodeview.com'>;> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Step 1: Create an object of BufferedWriter> >BufferedWriter f_writer> >=>new> BufferedWriter(>new> FileWriter(> >'/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'>));> >// Step 2: Write text(content) to file> >f_writer.write(text);> >// Step 3: Printing the content inside the file> >// on the terminal/CMD> >System.out.print(text);> >// Step 4: Display message showcasing> >// successful execution of the program> >System.out.print(> >'File is created successfully with the content.'>);> >// Step 5: Close the BufferedWriter object> >f_writer.close();> >}> >// Catch block to handle if exceptions occurs> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Print the exception on console> >// using getMessage() method> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >}> }> |
>
>出力
Linuxファイルシステム
File is created successfully with the content.>

次の例は、BufferedWriter クラスを使用してファイルに書き込む方法を示しています。また、コンテンツをファイルに書き込むには、FileWriter などの BufferedWriter クラスのオブジェクトを作成する必要があります。ただし、このクラスは、大きなバッファ サイズを使用してファイルに書き込む大きなコンテンツをサポートします。
方法 4: FileOutputStream クラスを使用する
生のストリーム データをファイルに書き込むために使用されます。 FileWriter クラスと BufferedWriter クラスはファイルにテキストのみを書き込むために使用されますが、FileOutputStream クラスを使用するとバイナリ データを書き込むことができます。
FileOutputStream クラスを使用してファイルにデータを書き込む方法を次の例に示します。また、データをファイルに書き込むために、ファイル名を使用してクラスのオブジェクトを作成する必要があります。ここでは、文字列の内容がバイト配列に変換され、ファイルに書き込まれます。 書く() 方法。
例:
ジャワ
// Java Program to Write into a File> // using FileOutputStream Class> // Importing java input output classes> import> java.io.FileOutputStream;> import> java.io.IOException;> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Assign the file content> >String fileContent =>'Welcome to geeksforgeeks'>;> >FileOutputStream outputStream =>null>;> >// Try block to check if exception occurs> >try> {> >// Step 1: Create an object of FileOutputStream> >outputStream =>new> FileOutputStream(>'file.txt'>);> >// Step 2: Store byte content from string> >byte>[] strToBytes = fileContent.getBytes();> >// Step 3: Write into the file> >outputStream.write(strToBytes);> >// Print the success message (Optional)> >System.out.print(> >'File is created successfully with the content.'>);> >}> >// Catch block to handle the exception> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Display the exception/s> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >// finally keyword is used with in try catch block> >// and this code will always execute whether> >// exception occurred or not> >finally> {> >// Step 4: Close the object> >if> (outputStream !=>null>) {> >// Note: Second try catch block ensures that> >// the file is closed even if an error> >// occurs> >try> {> >// Closing the file connections> >// if no exception has occurred> >outputStream.close();> >}> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Display exceptions if occurred> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >}> >}> >}> }> |
レカ映画女優
>
>出力
File is created successfully with the content.>
