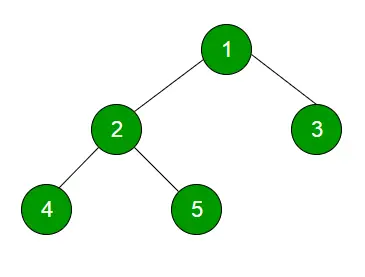
レベル順序のトラバーサル この手法は、同じレベルに存在するすべてのノードが次のレベルをトラバースする前に完全にトラバースされるように、ツリーをトラバースする方法として定義されます。
例:
推奨される練習レベルの順序トラバーサル 試してみましょう!入力:
出力:
1
23
4つ。
レベル順序トラバーサルはどのように機能しますか?
レベル順序トラバーサルの主な考え方は、より高いレベルのノードに移動する前に、より低いレベルのすべてのノードをトラバースすることです。これは、次のいずれかの方法で実行できます。
- 単純なもの (木の高さを見つけて各レベルを走査し、そのレベルのノードを出力する)
- キューを効率的に使用します。
レベル順序トラバーサル (単純なアプローチ):
探す 身長 木の。次に、レベルごとに、現在の高さを維持して再帰関数を実行します。ノードのレベルが一致するたびに、そのノードを出力します。
上記のアプローチの実装を以下に示します。
C++ // Recursive CPP program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include using namespace std; // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child class node { public: int data; node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level); int height(node* node); node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) cout << root->データ<< ' '; else if (level>1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root->right、レベル - 1); } } // ツリーの「高さ」、つまりルート ノードから // 最も遠いリーフ ノードまでの最長パスに沿ったノードの数を計算します。 int height(node* ノード) { if (node == NULL) は 0 を返します。 else { // 各サブツリーの高さを計算します int lheight = height(node->left); int rheight = 高さ(ノード->右); // 大きい方を使用します if (lheight> rheight) { return (lheight + 1); } else { return (rheight + 1); } } } // 指定されたデータと // NULL の左右のポインタを持つ新しいノードを割り当てるヘルパー関数。ノード* newNode(int data) { ノード* ノード = 新しいノード(); ノード -> データ = データ; ノード->左 = NULL; ノード->右 = NULL; 戻り値 (ノード); } // ドライバーコード int main() { node* root = newNode(1); ルート->左 = newNode(2); ルート->右 = newNode(3); ルート->左->左 = newNode(4); ルート->左->右 = newNode(5); コート<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra> C // Recursive C program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include #include // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level); int height(struct node* node); struct node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) printf('%d ', root->データ); else if (レベル> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root->right、レベル - 1); } } // ツリーの「高さ」を計算します -- // ルート ノードから最も遠い葉ノードまでの // 最長のパスに沿ったノードの数 int height(struct node* node) { if (node == NULL) 0 を返します。 else { // 各サブツリーの高さを計算します int lheight = height(node->left); int rheight = 高さ(ノード->右); // 大きい方を使用 if (lheight> rheight) return (lheight + 1); それ以外の場合は (rheight + 1) を返します。 } } // 指定されたデータと NULL の左右のポインタを持つ新しいノードを // 割り当てるヘルパー関数。 struct ノード* newNode(int data) { struct ノード* ノード = (struct ノード*)malloc(sizeof(struct ノード)); ノード->データ = データ; ノード->左 = NULL; ノード->右 = NULL; リターン (ノード); } // 上記の関数をテストするドライバー プログラム int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); ルート->左 = newNode(2); ルート->右 = newNode(3); ルート->左->左 = newNode(4); ルート->左->右 = newNode(5); printf('バイナリ ツリーのレベル順序トラバーサルは
'); printLevelOrder(ルート); 0を返します。 }>> ジャワ // Recursive Java program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class BinaryTree { // Root of the Binary Tree Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order traversal of tree void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number of // nodes along the longest path from the root node // down to the farthest leaf node. int height(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>rheight) return (lheight + 1); それ以外の場合は (rheight + 1) を返します。 } } // 現在のレベルでノードを出力します void printCurrentLevel(Node root, int level) { if (root == null) return; if (レベル == 1) System.out.print(root.data + ' '); else if (レベル> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, レベル - 1); } } // 上記の関数をテストするドライバー プログラム public static void main(String args[]) { BinaryTree Tree = new BinaryTree(); ツリー.ルート = 新しいノード(1); Tree.root.left = 新しいノード(2); Tree.root.right = 新しいノード(3); Tree.root.left.left = 新しいノード(4); Tree.root.left.right = 新しいノード(5); System.out.println('レベル順序走査' + 'バイナリ ツリーは '); ツリー.printLevelOrder(); } }>> パイソン # Recursive Python program for level # order traversal of Binary Tree # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Function to print level order traversal of tree def printLevelOrder(root): h = height(root) for i in range(1, h+1): printCurrentLevel(root, i) # Print nodes at a current level def printCurrentLevel(root, level): if root is None: return if level == 1: print(root.data, end=' ') elif level>1: printCurrentLevel(root.left, level-1) printCurrentLevel(root.right, level-1) # ツリーの高さ、つまりルート ノードから # 最も遠い葉までの最長パスに沿ったノードの数を計算します。 node def height(node): ノードが None の場合: return 0 else: # 各サブツリーの高さを計算します lheight = height(node.left) rheight = height(node.right) # lheight> rheight の場合は大きい方を使用します: return lheight+1 else: return rheight+1 # 上記の関数をテストするドライバー プログラム if __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root。 left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) print('バイナリ ツリーのレベル順序トラバーサルは -') printLevelOrder(root) # このコードは Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007) によって提供されています> C# // Recursive c# program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree using System; // Class containing left and right // child of current node and key value public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class GFG { // Root of the Binary Tree public Node root; public void BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order // traversal of tree public virtual void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) { printCurrentLevel(root, i); } } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- // the number of nodes along the longest // path from the root node down to the // farthest leaf node. public virtual int height(Node root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>rheight) { return (lheight + 1); } else { return (rheight + 1); } } } // 現在のレベルのノードを出力します public virtual void printCurrentLevel(Node root, int level) { if (root == null) { return; if (レベル == 1) { Console.Write(root.data + ' '); else if (レベル> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, レベル - 1); } } // ドライバーコード public static void Main(string[] args) { GFG ツリー = new GFG(); ツリー.ルート = 新しいノード(1); Tree.root.left = 新しいノード(2); Tree.root.right = 新しいノード(3); Tree.root.left.left = 新しいノード(4); Tree.root.left.right = 新しいノード(5); Console.WriteLine('バイナリ ツリーのレベル順序トラバーサル ' + ' は '); ツリー.printLevelOrder(); } } // このコードは Shrikant13 によって提供されました>>'JavaScriptrheight) return (lheight + 1); それ以外の場合は (rheight + 1) を返します。 } } // 現在のレベルのノードを出力します function printCurrentLevel(root , level) { if (root == null) return; if (レベル == 1) console.log(root.data + ' '); else if (レベル> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, レベル - 1); } } // 上記の関数をテストするドライバー プログラム root = new Node(1); root.left = 新しいノード(2); root.right = 新しいノード(3); root.left.left = 新しいノード(4); root.left.right = 新しいノード(5); console.log('バイナリ ツリーのレベル順トラバーサルは '); printLevelOrder(); // このコードは umadevi9616 によって提供されました>>'
出力 Level Order traversal of binary tree is 1 2 3 4 5>
時間計算量: O(N)、N は傾斜ツリー内のノードの数です。
補助スペース: O(1) 再帰スタックを考慮した場合、使用されるスペースは O(N) です。
たんぱく質脂肪です
を使用したレベル順序トラバーサル 列
上位レベルのノードにアクセスする前に、下位レベルのノードにアクセスする必要があります。この考え方はキューの考え方と非常に似ています。下位レベルのノードをキューにプッシュします。いずれかのノードにアクセスすると、そのノードをキューからポップし、そのノードの子をキューにプッシュします。
これにより、より高いレベルのノードよりも前に、より低いレベルのノードが訪問されることが保証されます。
上記のアプローチの実装を以下に示します。
C++ // C++ program to print level order traversal #include using namespace std; // A Binary Tree Node struct Node { int data; struct Node *left, *right; }; // Iterative method to find height of Binary Tree void printLevelOrder(Node* root) { // Base Case if (root == NULL) return; // Create an empty queue for level order traversal queueq; // ルートをキューに入れ、高さを初期化します。 q.push(root); while (q.empty() == false) { // キューの先頭を出力し、キューから削除 Node* node = q.front(); コート<< node->データ<< ' '; q.pop(); // Enqueue left child if (node->left != NULL) q.push(node->left); // 右の子をキューに入れる if (node->right != NULL) q.push(node->right); } } // 新しいツリー ノードを作成するユーティリティ関数 Node* newNode(int data) { Node* temp = new Node; 一時->データ = データ; 一時->左 = 一時->右 = NULL; 戻り温度; } // 上記の関数をテストするドライバー プログラム int main() { // 上の図に示すバイナリ ツリーを作成しましょう Node* root = newNode(1); ルート->左 = newNode(2); ルート->右 = newNode(3); ルート->左->左 = newNode(4); ルート->左->右 = newNode(5); コート<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; }> C // Iterative Queue based C program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree #include #include #define MAX_Q_SIZE 500 // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node* left; struct node* right; }; // Function prototypes struct node** createQueue(int*, int*); void enQueue(struct node**, int*, struct node*); struct node* deQueue(struct node**, int*); // Given a binary tree, print its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int rear, front; struct node** queue = createQueue(&front, &rear); struct node* temp_node = root; while (temp_node) { printf('%d ', temp_node->データ); // 左の子をキューに入れます if (temp_node->left) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->left); // 右の子をキューに入れます if (temp_node->right) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->right); // ノードをデキューして temp_node にします temp_node = deQueue(queue, &front); } } // ユーティリティ関数 struct node** createQueue(int* Front, int* Rear) { struct node** queue = (struct node**)malloc( sizeof(struct node*) * MAX_Q_SIZE); *フロント = *リア = 0; 戻り待ち行列。 } void enQueue(struct ノード** キュー, int* リア, 構造体ノード* new_node) { キュー[*リア] = new_node; (*後)++; struct ノード* deQueue(struct ノード** キュー, int* フロント) { (*フロント)++; キューを返す[*フロント - 1]; } // 指定されたデータと NULL の左右のポインタを持つ新しいノードを割り当てるヘルパー関数。 struct ノード* newNode(int data) { struct ノード* ノード = (struct ノード*)malloc(sizeof(struct ノード)); ノード->データ = データ; ノード->左 = NULL; ノード->右 = NULL; リターン (ノード); } // 上記の関数をテストするドライバー プログラム int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); ルート->左 = newNode(2); ルート->右 = newNode(3); ルート->左->左 = newNode(4); ルート->左->右 = newNode(5); printf('バイナリ ツリーのレベル順序トラバーサルは
'); printLevelOrder(ルート); 0を返します。 }>> ジャワ // Iterative Queue based Java program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; // Class to represent Tree node class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queueキュー = 新しいリンクリスト(); queue.add(ルート); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { //poll() は現在のヘッドを削除します。 ノード tempNode = queue.poll(); System.out.print(tempNode.data + ' '); // 左の子をキューに追加します if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.add(tempNode.left); } // 右の子をキューに追加します if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.add(tempNode.right); public static void main(String args[]) { // バイナリ ツリーの作成とノードの入力 // BinaryTree Tree_level = new BinaryTree(); Tree_level.root = 新しいノード(1); Tree_level.root.left = 新しいノード(2); Tree_level.root.right = 新しいノード(3); Tree_level.root.left.left = 新しいノード(4); Tree_level.root.left.right = 新しいノード(5); System.out.println('バイナリ ツリーのレベル順序トラバーサルは - '); ツリーレベル.printLevelOrder(); } }>> パイソン # Python program to print level # order traversal using Queue # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Iterative Method to print the # height of a binary tree def printLevelOrder(root): # Base Case if root is None: return # Create an empty queue # for level order traversal queue = [] # Enqueue Root and initialize height queue.append(root) while(len(queue)>0): # キューの先頭を出力し、 # キューから削除します print(queue[0].data, end=' ') node = queue.pop(0) # node.left が None でない場合、左側の子をキューに追加します: queue.append(node.left) # node.right が None でない場合、右の子をキューに追加します: queue.append(node.right) # 上記の関数をテストするドライバー プログラム if __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1 ) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) print('二分木のレベル順走査は - ') printLevelOrder(root) # このコードは Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007) によって提供されています>> C# // Iterative Queue based C# program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Class to represent Tree node public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal public class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order using // array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queueキュー = 新しいキュー(); キュー.エンキュー(ルート); while (queue.Count != 0) { ノード tempNode = queue.Dequeue(); Console.Write(tempNode.data + ' '); // 左の子をキューに入れます if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.Enqueue(tempNode.left); } // 右の子をキューに入れます if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.Enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // ドライバー コード public static void Main() { // バイナリ ツリーを作成し、 // ノードを入力 BinaryTree Tree_level = new BinaryTree(); Tree_level.root = 新しいノード(1); Tree_level.root.left = 新しいノード(2); Tree_level.root.right = 新しいノード(3); Tree_level.root.left.left = 新しいノード(4); Tree_level.root.left.right = 新しいノード(5); Console.WriteLine('バイナリ ツリーのレベル順序トラバーサル ' + ' は - '); ツリーレベル.printLevelOrder(); } } // このコードは PrinciRaj1992 によって提供されました>> JavaScript class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Class to represent a deque (double-ended queue) class Deque { constructor() { this.queue = []; } // Method to add an element to the end of the queue enqueue(item) { this.queue.push(item); } // Method to remove and return the first element of the queue dequeue() { return this.queue.shift(); } // Method to check if the queue is empty isEmpty() { return this.queue.length === 0; } } // Function to perform level order traversal of a binary tree function printLevelOrder(root) { // Create a deque to store nodes for traversal const queue = new Deque(); // Add the root node to the queue queue.enqueue(root); // Continue traversal until the queue is empty while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // Remove and get the first node from the queue const tempNode = queue.dequeue(); // Print the data of the current node console.log(tempNode.data + ' '); // Enqueue the left child if it exists if (tempNode.left !== null) { queue.enqueue(tempNode.left); } // Enqueue the right child if it exists if (tempNode.right !== null) { queue.enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // Create a binary tree and enter the nodes const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); // Print the level order traversal of the binary tree console.log('Level order traversal of binary tree is - '); printLevelOrder(root);> 出力
補助スペース: O(N) ここで、N はバイナリ ツリー内のノードの数です。